অক্ষিপট
এই নিবন্ধটি বাংলায় অনুবাদ করা প্রয়োজন। এই নিবন্ধটি বাংলা ব্যতীত অন্য কোন ভাষায় লেখা হয়েছে। নিবন্ধটি যদি ঐ নির্দিষ্ট ভাষা ব্যবহারকারীদের উদ্দেশ্যে লেখা হয়ে থাকে তবে, অনুগ্রহ করে নিবন্ধটি ঐ নির্দিষ্ট ভাষার উইকিপিডিয়াতে তৈরি করুন। অন্যান্য ভাষার উইকিপিডিয়ার তালিকা দেখুন এখানে। এই নিবন্ধটি পড়ার জন্য আপনি গুগল অনুবাদ ব্যবহার করতে পারেন। কিন্তু এ ধরনের স্বয়ংক্রিয় সরঞ্জাম দ্বারা অনুবাদকৃত লেখা উইকিপিডিয়াতে সংযোজন করবেন না, কারণ সাধারণত এই সরঞ্জামগুলোর অনুবাদ মানসম্পন্ন হয় না। |
| অক্ষিপট | |
|---|---|
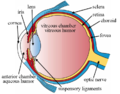
 Right human eye cross-sectional view, eyes vary significantly among animals. | |
| বিস্তারিত | |
| ধমনী | সেন্ট্রাল রেটিনাল আর্টারি |
| শনাক্তকারী | |
| মে-এসএইচ | D012160 |
| টিএ৯৮ | A15.2.04.002 |
| টিএ২ | 6776 |
| এফএমএ | FMA:58301 |
| শারীরস্থান পরিভাষা | |
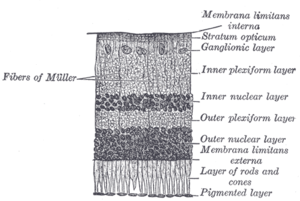
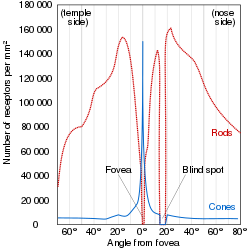
অক্ষিপট হলো মেরুদন্ডী প্রাণীদের চক্ষুগোলকের পিছনের দিকে অবস্থিত স্নায়ুকোষযুক্ত একটি পাতলা স্তর। মেরুদন্ডী প্রাণীদের ভ্রূণের বিকাশের সময় অক্ষিপট ও দর্শন স্নায়ু বর্ধিষ্ণু মস্তিস্কের অংশ হিসাবে বিকাশ লাভ করে। এটি কেন্দ্রীয় স্নায়ুতন্ত্রের অংশ।[১][২] মেরুদন্ডী প্রাণীদের অক্ষিপটে আলোক সংবেদী কোষ (দণ্ড কোষ বা রড কোষ এবং শঙ্কু কোষ বা কোন কোষ) রয়েছে, যাতে আলো পতিত হলে স্নায়ু উত্তেজনার সৃষ্টি হয়। এই স্নায়ুগত তাড়না রেটিনার অন্যান্য নিউরন দ্বারা বিশ্লেষণ করা হয়। অক্ষিপট হতে প্রাপ্ত সংকেত অক্ষিপটের গ্যাংলিয়া কোষে বৈদ্যুতিক বিভবের সৃষ্টি করে, যা চক্ষু স্নায়ুতে প্রবাহিত হয়।[৩]


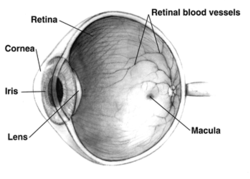
মানুষের অক্ষিপটের রক্তনালিকাগুলির বিন্যাস একেক মানুষের ক্ষেত্রে একেক রকম হয়ে থাকে। অক্ষিপটের রক্তনালিকার বিন্যাসের ভিত্তিতে জৈবমিতি পদ্ধতিতে মানুষের পরিচয় শনাক্ত করা যায়।

আরও চিত্র
[সম্পাদনা]-
The structures of the eye labeled
-
Another view of the eye and the structures of the eye labeled
-
Illustration of image as 'seen' by the retina independent of optic nerve and striate cortex processing.
আরও দেখুন
[সম্পাদনা]তথ্যসূত্র
[সম্পাদনা]- ↑ "Sensory Reception: Human Vision: Structure and function of the Human Eye" vol. 27, Encyclopaedia Britannica, 1987
- ↑ "সংরক্ষণাগারভুক্ত অনুলিপি"। ১১ মার্চ ২০১৩ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২৫ জুলাই ২০১৬।
- ↑ The Retinal Tunic. ওয়েব্যাক মেশিনে আর্কাইভকৃত ১৮ মে ২০০৭ তারিখে Virginia-Maryland Regional College of Veterinary Medicine
- ↑ Foundations of Vision ওয়েব্যাক মেশিনে আর্কাইভকৃত ৩ ডিসেম্বর ২০১৩ তারিখে, Brian A. Wandell
আরও পড়ুন
[সম্পাদনা]- S. Ramón y Cajal, Histologie du Système Nerveux de l'Homme et des Vertébrés, Maloine, Paris, 1911.
- Rodieck RW (১৯৬৫)। "Quantitative analysis of cat retinal ganglion cell response to visual stimuli"। Vision Res.। 5 (11): 583–601। ডিওআই:10.1016/0042-6989(65)90033-7। পিএমআইডি 5862581।
- Wandell, Brian A. (১৯৯৫)। Foundations of vision। Sunderland, Mass: Sinauer Associates। আইএসবিএন 0-87893-853-2।
- Wässle H, Boycott BB (১৯৯১)। "Functional architecture of the mammalian retina"। Physiol Rev.। 71 (2): 447–480। পিএমআইডি 2006220।
- Schulz HL, Goetz T, Kaschkoetoe J, Weber BH (২০০৪)। "The Retinome – Defining a reference transcriptome of the adult mammalian retina/retinal pigment epithelium"। BMC journals Genomics (about a transcriptome for eye color)। 5 (1): 50। ডিওআই:10.1186/1471-2164-5-50। পিএমআইডি 15283859। পিএমসি 512282
 ।
। - Retina John Dowling, Scholarpedia, 2(12):3487. doi:10.4249/scholarpedia.3487
- M.R.Khoshbin-e-Khoshnazar,"Quantum Superposition in the Retina:Evidences and Proposals".NeuroQuantology,12(1):97-101, 2014.
বহিঃসংযোগ
[সম্পাদনা]- Eye, Brain, and Vision - online book - by David Hubel
- Kolb, H., Fernandez, E., & Nelson, R. (2003). Webvision: The neural organization of the vertebrate retina. Salt Lake City, Utah: John Moran Eye Center, University of Utah. Retrieved July 22, 2014.
- Demo: Artificial Retina, MIT Technology Review, September 2004. Reports on implant research at Technology Review
- Successful photoreceptor transplantation, MIT Technology Review, November 2006. How stem cells might restore sight Technology Review
- Australian Vision Prosthesis Group ওয়েব্যাক মেশিনে আর্কাইভকৃত ১২ আগস্ট ২০১১ তারিখে, Graduate School of Biomedical Engineering, University of New South Wales
- RetinaCentral ওয়েব্যাক মেশিনে আর্কাইভকৃত ১৬ ডিসেম্বর ২০১৮ তারিখে, Genetics and Diseases of the Human Retina at University of Würzburg
- Retinal layers image. NeuroScience 2nd Ed at United States National Library of Medicine
- Jeremy Nathans's seminars: "The Vertebrate Retina: Structure, Function, and Evolution"
- Retina - Cell Centered Database
- টেমপ্লেট:BUHistology
- টেমপ্লেট:MedlinePlusEncyclopedia
টেমপ্লেট:Eye anatomy টেমপ্লেট:Visual pathways