ইসলামিক কায়রো
| ইউনেস্কো বিশ্ব ঐতিহ্যবাহী স্থান | |
|---|---|
 | |
| অবস্থান | Cairo Governorate, মিশর |
| অন্তর্ভুক্ত করে |
|
| মানদণ্ড | সাংস্কৃতিক: (i), (v), (vi) |
| সূত্র | 89 |
| তালিকাভুক্তকরণ | ১৯৭৯ (৩য় সভা) |
| আয়তন | ৫২৩.৬৬ হেক্টর (১,২৯৪.০ একর) |
| স্থানাঙ্ক | ৩০°০২′৪৫.৬১″ উত্তর ৩১°১৫′৪৫.৭৮″ পূর্ব / ৩০.০৪৬০০২৮° উত্তর ৩১.২৬২৭১৬৭° পূর্ব |
ইসলামিক কায়রো (আরবি: قاهرة المعز, অর্থ: আল-মুইজের কায়রো), যাকে ঐতিহাসিক কায়রো বা মধ্যযুগীয় কায়রোও বলা হয়, সাধারণভাবে মিশর-এর কায়রো-এর ঐতিহাসিক এলাকাগুলিকে বোঝায়, যেগুলি ১৮ এবং ২০ শতাব্দী শহরের আধুনিক সম্প্রসারণের আগে বিদ্যমান ছিল। শতাব্দী; বিশেষ করে পুরানো প্রাচীর ঘেরা শহরের চারপাশে এবং কায়রোর দুর্গের চারপাশে কেন্দ্রীয় অংশ। "ইসলামিক" কায়রো নামটি এলাকার মুসলমানদের বৃহত্তর বিশিষ্টতাকে বোঝায় না, বরং ইসলামের প্রাথমিক যুগে এর ভিত্তি থেকে শহরটির সমৃদ্ধ ইতিহাস এবং ঐতিহ্যকে বোঝায়, যখন এটিকে গিজা এবং মেমফিসের নিকটবর্তী প্রাচীন মিশরীয় স্থানগুলির সাথে আলাদা করে।[১][২] এই অঞ্চলটি ইসলামি বিশ্বের ঐতিহাসিক স্থাপত্যের বৃহত্তম এবং ঘন ঘনত্বের একটি ধারক।[১]:৭ এটি শত শত মসজিদ, সমাধি, মাদরাসা, প্রাসাদ, ক্যারাভানসরাই এবং মিশরের ইসলামী যুগের দুর্গ দ্বারা চিহ্নিত করা হয়েছে। ১৯৭৯ সালে, জাতিসংঘের শিক্ষা, বৈজ্ঞানিক ও সাংস্কৃতিক সংস্থা (UNESCO) ঐতিহাসিক কায়রোকে বিশ্ব সাংস্কৃতিক ঐতিহ্যবাহী স্থান হিসেবে ঘোষণা করে। এ সম্পর্কে তাদের বক্তব্য এ রুপ : "বিশ্বের প্রাচীনতম ইসলামি শহরগুলির মধ্যে একটি, যার বিখ্যাত মসজিদ, মাদরাসা, হাম্মাম এবং ঝর্ণা রয়েছে" এবং "ইসলামি বিশ্বের নতুন কেন্দ্র, ১৪ শতকে তার স্বর্ণযুগে পৌঁছেছে ।"[৩]
ইতিহাস[সম্পাদনা]
ফুসতাতের ভিত্তি এবং প্রাথমিক ইসলামী যুগ[সম্পাদনা]

The history of Cairo begins, in essence, with the conquest of Egypt by Muslim Arabs in 640, under the commander 'Amr ibn al-'As.[৪] Although Alexandria was the capital of Egypt at that time (and had been throughout the Ptolemaic, Roman, and Byzantine periods), the Arab conquerors decided to establish a new city called Fustat to serve as the administrative capital and military garrison center of Egypt. The new city was located near a Roman-Byzantine fortress known as Babylon on the shores of the Nile (now located in Old Cairo), southwest of the later site of Cairo proper (see below). The choice of this location may have been due to several factors, including its slightly closer proximity to Arabia and Mecca, the fear of strong remaining Christian and Hellenistic influence in Alexandria, and Alexandria's vulnerability to Byzantine counteroffensives arriving by sea (which did indeed occur).[৪][৫] Perhaps even more importantly, the location of Fustat at the intersection of Lower Egypt (the Nile Delta) and Upper Egypt (the Nile Valley further south) made it a strategic place from which to control a country that was centered on the Nile river, much as the Ancient Egyptian city of Memphis (located just south of Cairo today) had done.[৪][৫] (The pattern of founding new garrison cities inland was also one that was repeated throughout the Arab conquests, with other examples such as Qayrawan in Tunisia or Kufa in Iraq.[৫]) The foundation of Fustat was also accompanied by the foundation of Egypt's (and Africa's) first mosque, the Mosque of 'Amr ibn al-'As, which has been much rebuilt over the centuries but still exists today.[১]
Fustat quickly grew to become Egypt's main city, port, and economic center, with Alexandria becoming more of a provincial city.[৫] In 661 the Islamic world came under the control of the Ummayyads, based in their capital at Damascus, until their overthrow by the Abbasids in 750. The last Ummayyad caliph, Marwan II, made his last stand in Egypt but was killed on August 1st, 750.[৪] Thereafter Egypt, and Fustat, passed under Abbasid control. The Abbasids marked their new rule in Egypt by founding a new administrative capital called al-'Askar, slightly northeast of Fustat, under the initiative of their governor Abu 'Aun. The city was completed with the foundation of a grand mosque (called Jami' al-'Askar) in 786, and included a palace for the governor's residence, known as the Dar al-'Imara.[৪] Nothing of this city remains today, but the foundation of new administrative capitals just outside the main city became a recurring pattern in the history of the area. [[চিত্র:Kairo Ibn Tulun Moschee BW 5.jpg|থাম্ব|upright=1.2|ইবনে তুলুন মসজিদ, নবম শতাব্দীতে নির্মিত। এটি ইরাক--এর বাইরে সংরক্ষিত আব্বাসীয় স্থাপত্যের একটি বিরল এবং অসামান্য উদাহরণ। আহমদ ইবনে তুলুন ছিলেন একজন তুর্কি সামরিক কমান্ডার যিনি আব্বাসীয় ক্ষমতার দীর্ঘ সঙ্কটের সময় সামারায় আব্বাসীয় খলিফাদের সেবা করেছিলেন।[৬] He became governor of Egypt in 868 but quickly became its de facto independent ruler, while still acknowledging the Abbasid caliph's symbolic authority. He grew so influential that the caliph later allowed him to also take control of Syria in 878.[৪] During this period of Tulunid rule (under Ibn Tulun and his sons), Egypt became an independent state for the first time since Roman rule was established in 30 BC.[৪] Ibn Tulun founded his own new administrative capital in 870, called al-Qata'i, just northwest of al-Askar. It included a new grand palace (still called Dar al-'Imara), a hippodrome or military parade ground, amenities such as a hospital (bimaristan), and a great mosque which survives to this day, known as the Mosque of Ibn Tulun, built between 876 and 879.[৬][৪] Ibn Tulun died in 884 and his sons ruled for a few more decades until 905 when the Abbasids sent an army to reestablish direct control and burned al-Qata'i to the ground, sparing only the mosque.[৪] After this, Egypt was ruled for a while by another dynasty, the Ikhshidids, who ruled as Abbasid governors between 935 and 969. Some of their constructions, particularly under Abu al-Misk Kafur, a black eunuch (originally from Ethiopia) who ruled as regent during the later part of this period, may have influenced the future Fatimids' choice of location for their capital, since one of Kafur's great gardens along the Khalij canal was incorporated into the later Fatimid palaces.[৪]
Tআল-কাহিরা (কায়রো) এবং ফাতেমীয় আমলের প্রতিষ্ঠা[সম্পাদনা]
[[চিত্র:Cairo, porte settentrionali, 01.JPG|থাম্ব|Bab al-Futuh, one of the northern gates of Cairo built by the Fatimid vizier Badr al-Jamali in the late 11th century|বাম]]
The Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shi'a caliphate which was based in Ifriqiya (Tunisia), conquered Egypt in 969 CE during the reign of Caliph al-Mu'izz. Their army, composed mostly of North African Kutama Berbers, was led by the general Jawhar al-Siqilli. In 970, under instructions from al-Mu'izz, Jawhar planned, founded, and constructed a new city to serve as the residence and center of power for the Fatimid Caliphs. The city was named al-Mu'izziyya al-Qaahirah (আরবি: المعزية القاهرة), the "Victorious City of al-Mu'izz", later simply called "al-Qahira", which gave us the modern name of Cairo.[৭]:৮০

The city was located northeast of Fustat and of the previous administrative capitals built by Ibn Tulun and the Abbasids. Jawhar organized the new city so that at its center were the Great Palaces that housed the caliphs, their household, and the state's institutions.[৪] Two main palaces were completed: an eastern one (the largest of the two) and a western one, between which was an important plaza known as Bayn al-Qasrayn ("Between the Two Palaces"). The city's main mosque, the Mosque of al-Azhar, was founded in 972 as both a Friday mosque and as a center of learning and teaching, and is today considered one of the oldest universities in the world.[১] The city's main street, known today as Al-Mu'izz li-Din Allah Street (or al-Mu'zz street) but historically referred to as the Qasabah or Qasaba, ran from one of the northern city gates (Bab al-Futuh) to the southern gate (Bab Zuweila) and passed between the palaces via Bayn al-Qasrayn. Under the Fatimids, however, Cairo was a royal city which was closed to the common people and inhabited only by the Caliph's family, state officials, army regiments, and other people necessary to the operations of the regime and its city. Fustat remained for some time the main economic and urban center of Egypt. It was only later that Cairo grew to absorb other local cities, including Fustat, but the year 969 is sometimes considered the "founding year" of the current city.[৮]
Al-Mu'izz, and with him the administrative apparatus of the Fatimid Caliphate, left his former capital of Mahdia, Tunisia, in 972 and arrived in Cairo in June 973.[৭][৪] The Fatimid Empire quickly grew powerful enough to stand as a threat to the rival Sunni Abbasid Caliphate. During the reign of Caliph al-Mustansir (1036–1094), the longest of any Muslim ruler, the Fatimid Empire reached its peak but also began its decline.[৯] A few strong viziers, acting on behalf of the caliphs, managed to revive the empire's power on occasion. The Armenian vizier Badr al-Jamali (in office from 1073–1094) notably rebuilt the walls of Cairo in stone, with monumental gates, the remains of which still stand today and were expanded under later Ayyubid rule.[৪] The late 11th century was also a time of major events and developments in the region. It was at this time that the Great Seljuk (Turkish) Empire took over much of the eastern Islamic world. The arrival of the Turks, who were mainly Sunni Muslims, was a long-term factor in the so-called "Sunni Revival" which reversed the advance of the Fatimids and of Shi'a factions in the Middle East.[১০] In 1099 the First Crusade captured Jerusalem, and the new Crusader states became a sudden and serious threat to Egypt. New Muslim rulers such as Nur al-Din of the Turkish Zengid dynasty took charge of the overall offensive against the Crusaders.
In the 12th century the weakness of the Fatimids became so severe that under the last Fatmid Caliph, al-'Adid, they requested help from the Zengids to protect themselves from the King of Jerusalem, Amalric, while at the same time attempting to collude with the latter to keep the Zengids in check.[৭] In 1168, as the Crusaders marched on Cairo, the Fatimid vizier Shawar, worried that the unfortified city of Fustat would be used as a base from which to besiege Cairo, ordered its evacuation and then set the city ablaze. While historians debate the extent of the destruction (as Fustat appears to have continued to exist after this), the burning of Fustat nonetheless marks a pivotal moment in the decline of that city, which was later eclipsed by Cairo itself.[৪][১১] Eventually, Salah ad-Din (Saladin), a Zengid commander who was given the position of al-'Adid's vizier in Cairo, declared the end and dismantlement of the Fatimid Caliphate in 1171. Cairo thus returned to Sunni rule, and a new chapter in the history of Egypt, and of Cairo's urban history, opened.
আইয়ুবী ও মামলুক যুগে কায়রোর আরোহণ[সম্পাদনা]

Salah ad-Din's reign marked the beginning of the Ayyubid dynasty, which ruled over Egypt and Syria and carried forward the fight against the Crusaders. He also embarked on the construction of an ambitious new fortified Citadel (the current Citadel of Cairo) further south, outside the walled city, which would house Egypt's rulers and state administration for many centuries thereafter. This ended Cairo's status as an exclusive palace-city and started a process by which the city became an economic center inhabited by common Egyptians and open to foreign travelers.[১১] Over the subsequent centuries, Cairo developed into a full-scale urban center. The decline of Fustat over the same period paved the way for its ascendance. The Ayyubid sultans and their Mamluk successors, who were Sunni Muslims eager to erase the influence of the Shi'a Fatimids, progressively demolished and replaced the great Fatimid palaces with their own buildings.[৪] The Al-Azhar Mosque was converted to a Sunni institution, and today it is the foremost center for the study of the Qur'an and Islamic law in the Sunni Islamic world.[১]
In 1250 the Ayyubid dynasty faltered and power transitioned to a regime controlled by the Mamluks. The mamluks were soldiers who were purchased as young slaves (often from various regions of Central Eurasia) and raised to serve in the army of the sultan. They became a mainstay of the Ayyubid military under Sultan al-Salih and eventually became powerful enough to assume control of the state for themselves in a political crisis during the Seventh Crusade. Between 1250 and 1517, the throne passed from one mamluk to another in a system of succession that was generally non-hereditary, but also frequently violent and chaotic. Nonetheless, the Mamluk Empire continued many aspects of the Ayyubid Empire before it, and was responsible for repelling the advance of the Mongols in 1260 (most famously at the Battle of Ain Jalut) and for putting a final end to the Crusader states in the Levant.[১২]
Under the reign of the Mamluk sultan al-Nasir Muhammad (1293–1341, including interregnums), Cairo reached its apogee in terms of population and wealth.[৪] A commonly-cited estimate of the population towards the end of his reign, although difficult to evaluate, gives a figure of about 500,000, making Cairo the largest city in the world outside China at the time.[১৩][১৪] Despite being a largely military caste, the Mamluks were prolific builders and sponsors of religious and civic buildings. An extensive number of Cairo's historical monuments date from their era, including many of the most impressive.[৪][১] The city also prospered from the control of trade routes between the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean.[৪] After the reign of al-Nasir, however, Egypt and Cairo were struck by repeated epidemics of the plague, starting with the Black Death in the mid-14th century. Cairo's population declined and took centuries to recover, but it remained the major metropolis of the Middle East.[৪]
Under the Ayyubids and the later Mamluks, the Qasaba avenue became a privileged site for the construction of religious complexes, royal mausoleums, and commercial establishments, usually sponsored by the sultan or members of the ruling class. This is also where the major souqs of Cairo developed, forming its main economic zone of international trade and commercial activity.[৪][১] As the main street became saturated with shops and space for further development there ran out, new commercial structures were built further east, close to al-Azhar Mosque and to the shrine of al-Hussein, where the souq area of Khan al-Khalili, still present today, progressively developed.[১১] One important factor in the development of Cairo's urban character was the growing number of waqf establishments, especially during the Mamluk period. Waqfs were charitable trusts under Islamic law which set out the function, operations, and funding sources of the many religious/civic establishments built by the ruling elite. They were typically drawn up to define complex religious or civic buildings which combined various functions (e.g. mosque, madrasa, mausoleum, sebil) and which were often funded with revenues from urban commercial buildings or rural agricultural estates.[১৫] By the late 15th century Cairo also had high-rise mixed-use buildings (known as a rab', a khan or a wikala, depending on exact function) where the two lower floors were typically for commercial and storage purposes and the multiple stories above them were rented out to tenants.[১৬]
উসমানীয় সাম্রাজ্যের প্রাদেশিক রাজধানী হিসেবে কায়রো[সম্পাদনা]

Egypt was conquered by the Ottoman Empire in 1517, under Selim I, and remained under Ottoman rule for centuries. During this period, local elites fought ceaselessly among themselves for political power and influence; some of them of Ottoman origin, others from the Mamluk caste which continued to exist as part of the country's elites despite the demise of the Mamluk sultanate.[৪]
Cairo continued to be a major economic center and one of the empire's most important cities. It remained the principal staging point for the pilgrimage (Hajj) route to Mecca.[৪] While the Ottoman governors were not major patrons of architecture like the Mamluks, Cairo nonetheless continued to develop and new neighbourhoods did grow outside the old city walls.[৪][১] Ottoman architecture in Cairo continued to be heavily influenced and derived from the local Mamluk-era traditions rather than presenting a clear break with the past.[১] Some individuals, such as Abd ar-Rahman Katkhuda al-Qazdaghli, a mamluk official among the Janissaries in the 18th century, were prolific architectural patrons.[৪][১] Many old bourgeois or aristocratic mansions that have been preserved in Cairo today date from the Ottoman period, as do a number of sabil-kuttabs (a combination of water distribution kiosk and Qur'anic reading school).[১]
মুহাম্মদ আলি পাশা এবং খেদিভেসের অধীনে কায়রো[সম্পাদনা]

নেপোলিয়ন-এর ফরাসি সেনাবাহিনী ১৭৯৮ থেকে ১৮০১ সাল পর্যন্ত সংক্ষিপ্তভাবে মিশর দখল করে, তারপরে মুহাম্মদ আলি পাশা নামে অটোমান সেনাবাহিনীর একজন আলবেনিয়ান অফিসার কায়রোকে একটি স্বাধীন সাম্রাজ্যের রাজধানী করে তোলে যা ১৮০৫ থেকে ১৮৮২ সাল পর্যন্ত স্থায়ী ছিল। মিশর স্বাধীনতা না হওয়া পর্যন্ত শহরটি ১৯২২ সালে ব্রিটিশ নিয়ন্ত্রণে চলে আসে।

Under Muhammad Ali's rule the Citadel of Cairo was completely refurbished. Many of its disused Mamluk monuments were demolished to make way for his new mosque (the Mosque of Muhammad Ali) and other palaces. Muhammad Ali's dynasty also introduced a more purely Ottoman style of architecture, mainly in the late Ottoman Baroque style of the time.[১] One of his grandsons, Isma'il, as Khedive between 1864 and 1879, oversaw the construction of the modern Suez Canal. Along with this enterprise, he also undertook the construction of a vast new city in European style to the north and west of the historic center of Cairo. The new city emulated Haussman's 19th-century reforms of Paris, with grand boulevards and squares being part of the planning and layout.[৪] Although never fully completed to the extent of Isma'il's vision, this new city composes much of Downtown Cairo today. This left the old historic districts of Cairo, including the walled city, relatively neglected. Even the Citadel lost its status as the royal residence when Isma'il moved to the new Abdin Palace in 1874.[১]
ঐতিহাসিক স্থান এবং স্মৃতিস্তম্ভ[সম্পাদনা]
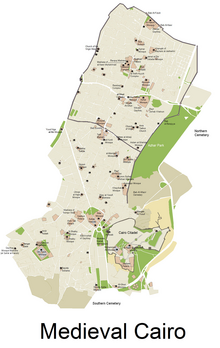
মসজিদ[সম্পাদনা]
মিশরের প্রথম মসজিদটি ফুসতাতে আমর ইবনে আল-আসের মসজিদ হলেও, ইবনে তুলুনের মসজিদটি তার আসল রূপ ধরে রাখা প্রাচীনতম মসজিদ এবং ইসলামি সভ্যতার ধ্রুপদী যুগ থেকে আব্বাসীয় স্থাপত্যের একটি বিরল উদাহরণ। এটি ৮৭৬-৮৭৯ খ্রিস্টাব্দে ইরাক-এর আব্বাসীয় রাজধানী সামারার দ্বারা অনুপ্রাণিত একটি শৈলীতে নির্মিত হয়েছিল।[১] এটি কায়রোর বৃহত্তম মসজিদগুলির মধ্যে একটি এবং প্রায়শই এটিকে সবচেয়ে সুন্দর হিসাবে উল্লেখ করা হয়।[১][১৭]
One of the most important and lasting institutions founded in the Fatimid period was the Mosque of al-Azhar, founded in 970 AD, which competes with the Qarawiyyin in Fes for the title of oldest university in the world.[১] Today, al-Azhar University is the foremost center of Islamic learning in the world and one of Egypt's largest universities with campuses across the country.[১] The mosque itself retains significant Fatimid elements but has been added to and expanded in subsequent centuries, notably by the Mamluk sultans Qaitbay and al-Ghuri and by Abd al-Rahman Katkhuda in the 18th century. Other extant monuments from the Fatimid era include the large Mosque of al-Hakim, the al-Aqmar mosque, Juyushi Mosque, Lulua Mosque, and the Mosque of Salih Tala'i.

The most prominent architectural heritage of medieval Cairo, however, dates from the Mamluk period, from 1250 to 1517 AD. The Mamluk sultans and elites were eager patrons of religious and scholarly life, commonly building religious or funerary complexes whose functions could include a mosque, madrasa, khanqah (for Sufis), water distribution centers (sabils), and mausoleum for themselves and their families.[১৫] Among the best-known examples of Mamluk monuments in Cairo are the huge Mosque-Madrasa of Sultan Hasan, the Mosque of Amir al-Maridani, the Mosque of Sultan al-Mu'ayyad (whose twin minarets were built above the gate of Bab Zuwayla), the Sultan Al-Ghuri complex, the funerary complex of Sultan Qaytbay in the Northern Cemetery, and the trio of monuments in the Bayn al-Qasrayn area comprising the complex of Sultan al-Mansur Qalawun, the Madrasa of al-Nasir Muhammad, and the Madrasa of Sultan Barquq. Some mosques include spolia (often columns or capitals) from earlier buildings built by the Romans, Byzantines, or Copts.[১]
Shrines and mausoleums[সম্পাদনা]
Islamic Cairo is also the location of several important religious shrines such as the al-Hussein Mosque (whose shrine is believed to hold the head of Husayn ibn Ali), the Mausoleum of Imam al-Shafi'i (founder of the Shafi'i madhhab, one of the primary schools of thought in Sunni Islamic jurisprudence), the Tomb of Sayyida Ruqayya, the Mosque of Sayyida Nafisa, and others.[১] Some of these shrines are located within the vast cemetery areas known as the City of the Dead or al-Qarafa in Arabic, which adjoin the historic city. The cemeteries date back to the foundation of Fustat, but many of the most prominent and famous mausoleum structures are from the Mamluk era.[১৮]
Walls and gates[সম্পাদনা]
When Cairo was founded as palace-city in 969 by the Fatimids, it was enclosed by a circuit of walls. These were rebuilt in stone in the late 11th century AD by the vizir Badr al-Gamali, parts of which survive today at Bab Zuwayla in the south and Bab al-Futuh and Bab al-Nasr in the north.[৪][১] The walls were extended and modified by the Ayyubids as part of Salah ad-Din's ambitious plan to protect both Cairo and Fustat by a single set of walls. Parts of these walls were recently excavated next to al-Azhar Park, including some Ayyubid gates like Bab al-Barqiya.[১]
দুর্গ[সম্পাদনা]
সালাহ আদ-দিন (সালাদিন) ১১৭৬ সালে মিশরের ক্ষমতার আসন হিসাবে কাজ করার জন্য একটি বিস্তৃত দুর্গ নির্মাণ শুরু করেছিলেন, যার নির্মাণ তার উত্তরসূরিদের অধীনে শেষ হয়েছিল।[১৯] এটি শহরকে উপেক্ষা করে কাছাকাছি মুকাত্তম পাহাড়ের একটি প্রমোনটরিতে অবস্থিত। ১৯ শতকের শেষ পর্যন্ত দুর্গটি মিশরের শাসকদের বাসস্থান ছিল এবং পরবর্তী শাসকদের অধীনে বারবার রূপান্তরিত হয়েছিল। উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে, মুহাম্মদ আলি পাশা ১৯ শতকের মুহাম্মদ আলি মসজিদ-টি তৈরি করেছিলেন যা এখনও শহরের আকাশপথে তার উঁচু স্থান থেকে আধিপত্য বিস্তার করছে ।[১]
বাজার এবং বাণিজ্যিক ভবন[সম্পাদনা]

কায়রোর অর্থনীতিতে ব্যবসা-বাণিজ্যের গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ভূমিকার কারণে মামলুক এবং পরবর্তী উসমানীয়রা বণিক ও দ্রব্যসামগ্রীর জন্য উইকলাস (ক্যারাভানসেরাই; খান নামেও পরিচিত) নির্মাণ করেছিল।[৪] সবচেয়ে বিখ্যাত এবং সর্বোত্তম-সংরক্ষিত উদাহরণ হল উইকালা আল-ঘুরি, যেটি আজকাল আল-তানুরা মিশরীয় হেরিটেজ ড্যান্স ট্রুপের নিয়মিত পরিবেশনারও আয়োজন করে।[২০] The famous Khan al-Khalili is a famous souq and commercial hub which also integrated caravanserais.[২১] Another example of historic commercial architecture is the 17th-century Qasaba of Radwan Bay, now part of the al-Khayamiyya area whose name comes from the decorative textiles (khayamiyya) still being sold here.[১]
সংরক্ষণের অবস্থা[সম্পাদনা]
এই ঐতিহাসিক এলাকাটির বেশির ভাগই অবহেলা এবং ক্ষয়ে ভুগছে, এটি মিশরীয় রাজধানীর অন্যতম দরিদ্র ও জনবহুল এলাকা।[২২] উপরন্তু, আল-আহরাম সাপ্তাহিক হিসাবে রিপোর্ট করা হয়েছে, আল-দার্ব আল-আহমার জেলায় ইসলামিক নিদর্শন এবং নিদর্শন চুরি তাদের দীর্ঘমেয়াদী সংরক্ষণকে হুমকির মুখে ফেলেছে।[২৩][২৪][২৫]
আরও দেখুন[সম্পাদনা]
তথ্যসূত্র[সম্পাদনা]
- ↑ ক খ গ ঘ ঙ চ ছ জ ঝ ঞ ট ঠ ড ঢ ণ ত থ দ ধ ন প ফ ব Williams, Caroline (২০১৮)। Islamic Monuments in Cairo: The Practical Guide (7th সংস্করণ)। Cairo: The American University in Cairo Press।
- ↑ Planet, Lonely। "Islamic Cairo in Cairo, Egypt"। Lonely Planet (ইংরেজি ভাষায়)। ২০১৯-১১-১৮ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০১৯-১১-১৮।
- ↑ UNESCO, Decision Text, World Heritage Centre, retrieved 21 July 2017
- ↑ ক খ গ ঘ ঙ চ ছ জ ঝ ঞ ট ঠ ড ঢ ণ ত থ দ ধ ন প ফ ব ভ ম য র Raymond, André. 1993. Le Caire. Fayard.
- ↑ ক খ গ ঘ Kennedy, Hugh (২০০৭)। The Great Arab Conquests: How the Spread of Islam Changed the World We Live In। Weidenfeld & Nicolson।
- ↑ ক খ Swelim, Tarek (২০১৫)। Ibn Tulun: His Lost City and Great Mosque। The American University in Cairo Press।
- ↑ ক খ গ Brett, Michael (২০১৭)। The Fatimid Empire। Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press।
- ↑ Irene Beeson (সেপ্টেম্বর–অক্টোবর ১৯৬৯)। "Cairo, a Millennial"। Saudi Aramco World। পৃষ্ঠা 24, 26–30। ২০০৭-০৯-৩০ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০০৭-০৮-০৯।
- ↑ "Fāṭimid Dynasty | Islamic dynasty"। Encyclopedia Britannica (ইংরেজি ভাষায়)। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০১৯-১১-১৬।
- ↑ Lewis, Bernard (১৯৯৫)। The Middle East: A Brief History of the Last 2,000 Years। Scribner।
- ↑ ক খ গ Denoix, Sylvie; Depaule, Jean-Charles; Tuchscherer, Michel, সম্পাদকগণ (১৯৯৯)। Le Khan al-Khalili et ses environs: Un centre commercial et artisanal au Caire du XIIIe au XXe siècle। Cairo: Institut français d'archéologie orientale।
- ↑ Clot, André (১৯৯৬)। L'Égypte des Mamelouks: L'empire des esclaves, 1250–1517। Perrin।
- ↑ Abu-Lughod, Janet (১৯৭১)। Cairo: 1001 Years of the City Victorious। Princeton University Press। পৃষ্ঠা 37।
- ↑ Shillington, Kevin (২০০৫)। Encyclopedia of African History। I। Taylor & Francis। পৃষ্ঠা 342।
- ↑ ক খ Behrens-Abouseif, Doris. 2007. Cairo of the Mamluks: A History of Architecture and its Culture. Cairo: The American University in Cairo Press.
- ↑ Mortada, Hisham (২০০৩)। Traditional Islamic principles of built environment। Routledge। পৃষ্ঠা viii। আইএসবিএন 0-7007-1700-5।
- ↑ O'Neill, Zora et al. 2012. Lonely Planet: Egypt (11th edition), p. 87.
- ↑ El Kadi, Galila; Bonnamy, Alain (২০০৭)। Architecture for the Dead: Cairo's Medieval Necropolis। Cairo: The American University in Cairo Press।
- ↑ Rabat, Nasser O. (১৯৯৫)। The Citadel of Cairo: A New Interpretation of Royal Mamluk Architecture। E.J. Brill।
- ↑ O'Neill, Zora et al. 2012. Lonely Planet: Egypt (11th edition), p. 81.
- ↑ Denoix, Sylvie; Depaule, Jean-Charles; Tuchscherer, Michel, সম্পাদকগণ (১৯৯৯)। Le Khan al-Khalili et ses environs: Un centre commercial et artisanal au Caire du XIIIe au XXe siècle। Cairo: Institut français d'archéologie orientale।
- ↑ Ancient Cairo: Preserving a Historical Heritage, Qantara, 2006.
- ↑ Unholy Thefts ওয়েব্যাক মেশিনে আর্কাইভকৃত ২০১৩-০৬-০৫ তারিখে Al-Ahram Weekly, Nevine El-Aref, 26 June – 2 July 2008 Issue No. 903.
- ↑ "Al-Darb Al-Ahmar District Mosques"। World Monuments Fund।
- ↑ Wilton-Steer, Harry Johnstone, photography by Christopher (মার্চ ২১, ২০১৮)। "Alive with artisans: Cairo's al-Darb al-Ahmar district – a photo essay" – www.theguardian.com-এর মাধ্যমে।
বহিঃসংযোগ[সম্পাদনা]
 উইকিমিডিয়া কমন্সে ইসলামিক কায়রো সম্পর্কিত মিডিয়া দেখুন।
উইকিমিডিয়া কমন্সে ইসলামিক কায়রো সম্পর্কিত মিডিয়া দেখুন।
 উইকিভ্রমণ থেকে Islamic Cairo ভ্রমণ নির্দেশিকা পড়ুন।
উইকিভ্রমণ থেকে Islamic Cairo ভ্রমণ নির্দেশিকা পড়ুন।






