নাগর্নো-কারাবাখ সংঘাত
| নাগর্নো-কারাবাখ | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| মূল যুদ্ধ: সোভিয়েত-পরবর্তী সংঘাত | |||||||||
 এ অঞ্চলের বর্তমান সামরিক অবস্থা, বিস্তারিত মানচিত্রের জন্য এখানে দেখুন | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| বিবাদমান পক্ষ | |||||||||
|
বিদেশী যোদ্ধা অস্ত্র সরবরাহ কূটনৈতিক সমর্থন |
Foreign fighters Arms suppliers Diplomatic support Supported by: | ||||||||
| জড়িত ইউনিট | |||||||||
|
আর্মেনীয় সশস্ত্র বাহিনী |
| ||||||||
| শক্তি | |||||||||
|
২০১৮: ৬৫,০০০ (সক্রিয় সৈন্য)[৩৫][ঙ] ১৯৯৩-১৯৯৪: ৩০,০০০–৪০,০০০[৩৮][৩৯] |
২০১৯: ৬৬,৯৫০ (সক্রিয় সৈন্য)[৪০] ১৯৯৩-১৯৯৪: ৪২,০০০–৫৬,০০০[৩৯][৩৮][৪১] | ||||||||
| হতাহত ও ক্ষয়ক্ষতি | |||||||||
|
২৮,০০০–৩৮,০০০ নিহত (১৯৮৮–১৯৯৪)[৪৬] ৩,০০০ নিহত (মে ১৯৯৪ – আগষ্ট ২০০৯)[৪৭] ৫৪১–৫৪৮+ নিহত (২০১০–২০১৯)[৪৮] ৭,৭১৭ নিহত (২০২০)[৪৯] ৪৪ নিহত (২০২১-২০২২)[৫০] | |||||||||
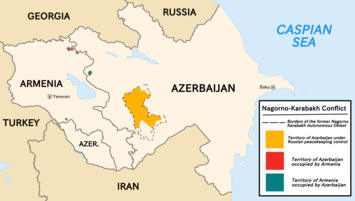
নাগোর্নো-কারাবাখ দ্বন্দ্ব [চ] হলো আর্মেনিয়া এবং আজারবাইজানের মধ্যে একটি জাতিগত এবং আঞ্চলিক দ্বন্দ্ব যা নাগোর্নো-কারাবাখের বিতর্কিত অঞ্চলে সংঘটিত হচ্ছে। এ অঞ্চলের বেশিরভাগ এলাকাই জাতিগত আর্মেনিয়ানদের দ্বারা অধ্যুষিত। নাগোর্নো-কারাবাখ অঞ্চলটি সম্পূর্ণরূপে কার্যত আর্টসখ প্রজাতন্ত্রের দ্বারা নিয়ন্ত্রিত, কিন্তু আন্তর্জাতিকভাবে আজারবাইজানের অংশ হিসাবে স্বীকৃত। আজারবাইজান নাগোর্নো-কারাবাখ অঞ্চলের অবশিষ্টাংশের পাশাপাশি আশেপাশের সাতটি জেলা নিয়ন্ত্রণ করে।
২০ শতকের গোড়ার দিকে এই সংঘাতের উৎপত্তি হয়েছে, কিন্তু বর্তমান সংঘাত ১৯৮৮ সালে শুরু হয়েছিল, যখন কারাবাখ আর্মেনীয়রা সোভিয়েত আজারবাইজান থেকে সোভিয়েত আর্মেনিয়াতে অঞ্চলটি হস্তান্তরের দাবি করেছিল। 1990-এর দশকের গোড়ার দিকে সোভিয়েত ইউনিয়নের বিলুপ্তির পর সংঘাতটি একটি পূর্ণাঙ্গ যুদ্ধে রূপ নেয়। প্রথম নাগর্নো-কারাবাখ যুদ্ধে হাজার হাজার মানুষ নিহত হয়। যুদ্ধটি আর্মেনিয়া জিতেছিল। আর্মেনিয়া
পরবর্তীতে সোভিয়েত যুগের নাগর্নো-কারাবাখের আশেপাশের অঞ্চলগুলি দখল নেয়করে।
জাতিগত আজারবাইজানিদের আর্মেনিয়ান-নিয়ন্ত্রিত এলাকা থেকে বহিষ্কার করা হয়েছিল, আর জাতিগত আর্মেনিয়ানদের আজারবাইজান থেকে বহিষ্কার করা হয়েছিল। বিশকেকে ১৯৯৪ সালে স্বাক্ষরিত প্রথম যুদ্ধের সমাপ্তি যুদ্ধবিরতির ফলে দুই দশকের জন্য আপেক্ষিক স্থিতিশীলতার এসেছিল। তবে ২০১০ এর দশকে উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে অবনতি হয়েছিল। এপ্রিল ২০১৬-এ চার দিন স্থায়ী সংঘাতের ফলে শত শত হতাহতের ঘটনা ঘটে এবং সীমান্ত রেখায় সামান্য পরিবর্তন হয়।
২০২০ সালের শেষের দিকে, বড় আকারের দ্বিতীয় নাগর্নো-কারাবাখ যুদ্ধের ফলে হাজার হাজার হতাহতের ঘটনা ঘটে এবং একটি আজারবাইজানিদের উল্লেখযোগ্য বিজয় ঘটে। ১০ নভেম্বর একটি ত্রিপক্ষীয় যুদ্ধবিরতি চুক্তির মাধ্যমে একটি যুদ্ধবিরতি প্রতিষ্ঠিত হয়েছিল, যার ফলে আজারবাইজান নাগোর্নো-কারাবাখের চারপাশের সমস্ত অধিকৃত অঞ্চল পুনরুদ্ধার করে এবং সেইসাথে নাগোর্নো-কারাবাখের এক-তৃতীয়াংশ দখল করে নেয়। [৫৫] নাগর্নো-কারাবাখ এবং আর্মেনিয়ান-আজারবাইজানি সীমান্তে যুদ্ধবিরতি লঙ্ঘন ২০২০ সালের যুদ্ধের পরেও অব্যাহত ছিল, এবং মাঝে মাঝে হতাহতের ঘটনা ঘটতে থাকে।
২০২০ সালের যুদ্ধের পর থেকে, আজারবাইজান তার আদিবাসী আর্মেনিয়ান বাসিন্দাদের বিশেষ মর্যাদা বা স্বায়ত্তশাসনের প্রস্তাব প্রত্যাহার করেছে এবং পরিবর্তে আজারবাইজানে তাদের "একীকরণের" উপর জোর দিয়েছে। [৫৬] [৫৭] ২০২২ সালের ডিসেম্বর থেকে, আজারবাইজান ২০২০ সালের যুদ্ধবিরতি চুক্তি এবং আন্তর্জাতিক আইনী বিধি লঙ্ঘন করে আর্টসাখ প্রজাতন্ত্রকে বহির্বিশ্ব থেকে অবরুদ্ধ করে রাখে।
১৯ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩-এ, ২০২০ যুদ্ধবিরতি শর্ত লঙ্ঘন করে, [৫৮] [৫৯] আজারবাইজান নাগর্নো-কারাবাখ-এ একটি বড় আকারের সামরিক আক্রমণ শুরু করে। [৬০] [৬১] [৬২] [৬৩] [৬৪] আক্রমণ শুরু হওয়ার একদিন পরে, ২০ সেপ্টেম্বর, নাগর্নো-কারাবাখে রাশিয়ান শান্তিরক্ষা কমান্ডের মধ্যস্থতায় নাগর্নো-কারাবাখে শত্রুতা সম্পূর্ণ বন্ধ করার বিষয়ে দুই দেশ একটি চুক্তিতে পৌঁছেছিল। [৬৫] [৬৬] আজারবাইজান ২১ সেপ্টেম্বর ইয়েভলাখে আর্টসাখ আর্মেনিয়ান সম্প্রদায়ের প্রতিনিধিদের সাথে একটি বৈঠক করে এবং পরের মাসে আরও একটি বৈঠক অনুষ্ঠিত হওয়ার বিষয়টি জানানো হয়। [৬৭] [৬৮]
২৮ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩ তারিখে আর্টসখের সভাপতি কর্তৃক জারি করা একটি ডিক্রি অনুসারে, ১ জানুয়ারী ২০২৪ এর মধ্যে আর্টসখের অস্তিত্ব বিলুপ্ত হয়ে যাবে [৬৯]
তথ্যসূত্র
[সম্পাদনা]- ↑ উদ্ধৃতি ত্রুটি:
<ref>ট্যাগ বৈধ নয়;Matveevaনামের সূত্রটির জন্য কোন লেখা প্রদান করা হয়নি - ↑ উদ্ধৃতি ত্রুটি:
<ref>ট্যাগ বৈধ নয়;Panossianনামের সূত্রটির জন্য কোন লেখা প্রদান করা হয়নি - ↑ Shogren, Elizabeth (২১ সেপ্টেম্বর ১৯৯০)। "Armenians Wage Hunger Strike in Regional Dispute: Soviet Union: Five threaten to starve themselves to death unless Moscow ends military rule in Azerbaijan enclave."। Los Angeles Times।
- ↑ Cornell, Svante E. (১৯৯৯)। "The Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict" (পিডিএফ)। Report no. 46, Department of East European Studies। Uppsala University। পৃষ্ঠা 26।
Sporadic clashes became frequent by the first months of 1991, with an ever-increasing organization of paramilitary forces on the Armenian side, whereas Azerbaijan still relied on the support of Moscow. [...] In response to this development, a joint Soviet and Azerbaijani military and police operation directed from Moscow was initiated in these areas during the Spring and Summer of 1991.
- ↑ Papazian, Taline (২০০৮)। "State at War, State in War: The Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict and State-Making in Armenia, 1991–1995"। The Journal of Power Institutions in Post-Soviet Societies (8): 25। ডিওআই:10.4000/pipss.1623
 ।
। ...units of the 4th army stationed in Azerbaijan and Azeri OMONs were used in “Operation Ring”, to empty a number of Armenian villages in Nagorno-Karabakh in April 1991.
- ↑ Murphy, David E. (১৯৯২)। "Operation 'Ring': The Black Berets in Azerbaijan"। The Journal of Soviet Military Studies। 5 (1): 93। ডিওআই:10.1080/13518049208430053।
...Operation 'Ring' as a combined Soviet-Azerbaijan operation to weaken Armenian resistance in the Nagorno-Karabakh enclave.
- ↑ "Принуждение к конфликту" [Coercion to conflict]। Kommersant (Russian ভাষায়)। ১৬ অক্টোবর ২০২০। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২১ এপ্রিল ২০২১।
- ↑ Kramer, Andrew E. (২৯ জানুয়ারি ২০২১)। "Armenia and Azerbaijan: What Sparked War and Will Peace Prevail?"। The New York Times। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ৪ মার্চ ২০২১।
Armenia has said that Turkey was directly involved in the fighting in and around Nagorno-Karabakh, and that a Turkish F-16 fighter shot down an Armenian jet. Turkey denied those accusations.
- ↑ Tsvetkova, Maria; Auyezov, Olzhas (৯ নভেম্বর ২০২০)। "Analysis: Russia and Turkey keep powder dry in Nagorno-Karabakh conflict"। Reuters। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ৪ মার্চ ২০২১।
Turkey's support for Azerbaijan has been vital, and Azerbaijan's superior weaponry and battlefield advances have reduced its incentive to reach a lasting peace deal. Ankara denies its troops are involved in fighting but Aliyev has acknowledged some Turkish F-16 fighter jets remained in Azerbaijan after a military drill this summer, and there are reports of Russian and Turkish drones being used by both sides.
- ↑ Rudolph, Joseph Russell, সম্পাদক (২০০৩)। Encyclopedia of Modern Ethnic Conflicts। Greenwood Press। পৃষ্ঠা 208। আইএসবিএন 978-0313313813।
When the Soviet Union broke up in 1991 [...] the Karabakh conflict escalated further, from guerrilla warfare to full-scale conventional combat.
- ↑ Tharoor, Ishaan (এপ্রিল ৫, ২০১৬)। "The crisis over Nagorno-Karabakh, explained"। Washington Post। ২৪ জুলাই ২০২০ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
- ↑ "The Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict: A Visual Explainer"। International Crisis Group। ২৯ জুন ২০২০ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
- ↑ "Armenia-Azerbaijan arms race undercuts peace prospects"। Emerald Expert Briefings। Oxford Analytica। আগস্ট ১১, ২০১৭। ডিওআই:10.1108/OXAN-DB223736।
As low-intensity fighting continues...
- ↑ Anishchuk, Alexei (ডিসেম্বর ১০, ২০১০)। "Armenia says to recognise Karabakh in case of war"। Reuters। ২৪ আগস্ট ২০২০ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
Low-intensity skirmishes since 1994...
- ↑ "The Azerbaijan-Armenia conflict hints at the future of war"। The Economist। অক্টোবর ১০, ২০২০।
The real war, which began on September 27th,...
- ↑ Hauer, Neil (অক্টোবর ৯, ২০২০)। "Caucasus war a result of US retreat from the world"। Asia Times।
The past two weeks have provided one of the starkest examples of the consequences of this: the re-eruption of full-scale war between Armenia and Azerbaijan over the disputed territory of Nagorno-Karabakh.
- ↑ "Armenia-Azerbaijan: Almost 100 killed in overnight clashes"। BBC। সেপ্টেম্বর ১৪, ২০২২।
- ↑ Lister, Tim; Mezzofiore, Gianluca; Edwards, Christian; Chernova, Anna; Walsh, Nick Paton। "Azerbaijan launches operation against Armenian forces in Nagorno-Karabakh"। CNN। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১৯ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩।
- ↑ Broers, Laurence (২০০৫)। "The limits of leadership: Elites and societies in the Nagorny Karabakh peace process" (পিডিএফ)। Accord। London: Conciliation Resources: 8। আইএসএসএন 1365-0742। ১৮ ফেব্রুয়ারি ২০১৭ তারিখে মূল (পিডিএফ) থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১৭ ফেব্রুয়ারি ২০১৭।
Overlaying what is fundamentally a territorial dispute are the consequences of the 1991–94 war: a decisive Armenian military victory resulting in Armenian control of Nagorny Karabakh and the further occupation of seven districts surrounding it.
- ↑ Mirovalev, Mansur (এপ্রিল ১৯, ২০১৬)। "Here's why a 'frozen' conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan has gotten hot"। Los Angeles Times।
The 1994 cease-fire [...] ended in political stalemate.
- ↑ The Caucasus and Central Asia: Transitioning to Emerging Markets (পিডিএফ)। International Monetary Fund। এপ্রিল ২০১৪। পৃষ্ঠা 72। আইএসবিএন 978-1484305140। ডিওআই:10.5089/9781484305140.087।
Armenia and Azerbaijan have been in a cold war since the cessation of large-scale conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh during 1988–94...
[স্থায়ীভাবে অকার্যকর সংযোগ] - ↑ Broers, Laurence (১২ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০১২)। "Armenia and Azerbaijan: what can societies do when political judgement errs?"। opendemocracy.net। openDemocracy। ২৪ আগস্ট ২০২০ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
...as cold war between Armenia and Azerbaijan deepens.
- ↑ Tchilingirian, Hratch (১৯৯৯)। "Nagorno Karabagh: Transition and the elite"। Central Asian Survey। 18 (4): 450। ডিওআই:10.1080/713656168।
As characterized by Karabagh's defence minister, the current post-war situation in the region is 'a cold war between Azerbaijan and Karabagh'.
- ↑ Bodner, Matthew (নভেম্বর ২১, ২০১৬)। "Russia Emerges as Winner in Arms Race Between Armenia and Azerbaijan"। The Moscow Times। ৫ আগস্ট ২০২০ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
- ↑ Mutschler, Max; Bales, Marius (ফেব্রুয়ারি ২০২০)। "Global Militarisation Index 2019" (পিডিএফ)। Bonn International Center for Conversion। পৃষ্ঠা 2। আইএসএসএন 2521-7844। ৬ আগস্ট ২০২১ তারিখে মূল (পিডিএফ) থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২৯ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩।
The unresolved secessionist conflict between Armenia (position 3) and Azerbaijan (position 10) over the Nagorno-Karabakh region continues to keep militarisation in the South Caucasus at a very high level.
- ↑ de Waal, Thomas (৩ এপ্রিল ২০১৬)। "Nagorno-Karabakh's cocktail of conflict explodes again"। BBC News। ২৮ মার্চ ২০১৯ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
The so-called Line of Contact between the two sides became the most militarised zone in the wider Europe, bristling with tanks and heavy artillery.
- ↑ "'Extremely painful': Armenia orders end to fighting with Azerbaijan over Nagorno-Karabakh"। Global News (ইংরেজি ভাষায়)। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০২০-১১-১০।
- ↑ "As Azerbaijan pushes advantage against Armenia, Russia's role again under scrutiny | Eurasianet"। eurasianet.org।
- ↑ Joshua Kucera (১৪ মে ২০২১)। "Armenia and Azerbaijan in new border crisis"। Eurasianet। ১৪ মে ২০২১ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১৪ মে ২০২১।
- ↑ "European Parliament resolution on prisoners of war in the aftermath of the most recent conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan (2021/2693(RSP))" (সংবাদ বিজ্ঞপ্তি)। European Parliament। ১৯ মে ২০২১। ২৬ মে ২০২১ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২৬ মে ২০২১।
On 12 May 2021, troops from Azerbaijan temporarily entered the territory of Armenia, which amounts to a violation of the territorial integrity of Armenia and of international law
- ↑ "Macron: Azerbaijani armed forces have crossed into Armenian territory. They must withdraw immediately. I say again to the Armenian people: France stands with you in solidarity and will continue to do so"। ২৪ মে ২০২১ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১৪ মে ২০২১।
- ↑ "Armenian separatists in Karabakh surrender and agree to ceasefire with Azerbaijan"। Reuters। ২০ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩। ২০ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩।
Under the agreement, confirmed by both sides and effective from 1 pm (0900 GMT) on Wednesday, separatist forces will disband and disarm and talks on the future of the region and the ethnic Armenians who live there will start on Thursday.
- ↑ "Karabakh Separatists To Hold Integration Talks With Azerbaijan Thursday"। Barron's। ২০ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩। ২০ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩।
- ↑
Trenin, Dmitri V. (২০১১)। Post-Imperium: A Eurasian Story। Brookings Institution Press। পৃষ্ঠা 67। আইএসবিএন 978-0870033452।
Armenia is de facto united with Nagorno-Karabakh, an unrecognized state, in a single entity.
- Mulcaire, Jack (৯ এপ্রিল ২০১৫)। "Face Off: The Coming War between Armenia and Azerbaijan"। The National Interest। ৩ জানুয়ারি ২০১৭ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১৪ ডিসেম্বর ২০১৬।
The mostly Armenian population of the disputed region now lives under the control of the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic, a micronation that is supported by Armenia and is effectively part of that country.
- Cornell, Svante (২০১১)। Azerbaijan Since Independence। New York: M.E. Sharpe। পৃষ্ঠা 135। আইএসবিএন 978-0-7656-3004-9।
Following the war, the territories that fell under Armenian control, in particular Mountainous Karabakh itself, were slowly integrated into Armenia. Officially, Karabakh and Armenia remain separate political entities, but for most practical matters the two entities are unified."
- Mulcaire, Jack (৯ এপ্রিল ২০১৫)। "Face Off: The Coming War between Armenia and Azerbaijan"। The National Interest। ৩ জানুয়ারি ২০১৭ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১৪ ডিসেম্বর ২০১৬।
- ↑ Abrahamyan, Eduard (৮ জানুয়ারি ২০১৮)। "Russian Loan Allows Armenia to Upgrade Military Capabilities"। CACI Analyst। Central Asia-Caucasus Institute। ৫ আগস্ট ২০২০ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
While often portrayed as separate forces, Armenia's Armed Forces and the “Artsakh Defense Army,” totaling up to 65,000 active personnel, are in practice one force with a single Command-and-Control (C2) system.
- ↑ International Institute for Strategic Studies (২০১৯)। The Military Balance 2019। London: Routledge। পৃষ্ঠা 184। আইএসবিএন 978-1857439885।
- ↑ Blandy, C. W. (২০০৮)। Azerbaijan: Is War Over Nagornyy Karabakh a Realistic Option? (পিডিএফ)। Advanced Research and Assessment Group, Defence Academy of the United Kingdom। পৃষ্ঠা 14। আইএসবিএন 978-1905962495। ২০১৬-০৪-১৫ তারিখে মূল (পিডিএফ) থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
- ↑ ক খ উদ্ধৃতি ত্রুটি:
<ref>ট্যাগ বৈধ নয়;SIPRI1994নামের সূত্রটির জন্য কোন লেখা প্রদান করা হয়নি - ↑ ক খ উদ্ধৃতি ত্রুটি:
<ref>ট্যাগ বৈধ নয়;CaucasianKnotনামের সূত্রটির জন্য কোন লেখা প্রদান করা হয়নি - ↑ International Institute for Strategic Studies (১৫ ফেব্রুয়ারি ২০১৯)। The Military Balance 2019। London: Routledge। পৃষ্ঠা 185। আইএসবিএন 978-1857439885।
- ↑ "SIPRI Yearbook 1995"। sipri.org। Stockholm International Peace Research Institute। পৃষ্ঠা 28। ২৬ আগস্ট ২০২০ তারিখে মূল (পিডিএফ) থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। Table of conflict locations with at least one major armed conflict in 1994
- ↑ de Waal 2003, পৃ. 285।
- ↑ Winds of Change in Nagorno Karabakh ওয়েব্যাক মেশিনে আর্কাইভকৃত ২০১১-১২-০৬ তারিখে. Euronews. 28 November 2009.
- ↑ Uppsala Conflict Data Program, Republic of Nagorno-Karabakh – civilians, viewed 2013-05-03
- ↑ "Azerbaijani Soldier Shot Dead by Armenian Forces"। Naharnet। ১৬ অক্টোবর ২০১৪ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২২ অক্টোবর ২০১৪।
- ↑ See [৪২][৪৩][৪৪][৪৫]
- ↑ "Armenia and Azerbaijan: Preventing War" (পিডিএফ)। Europe Briefing N°60। International Crisis Group। ৮ ফেব্রুয়ারি ২০১১। পৃষ্ঠা 3। ২০ মে ২০১৬ তারিখে মূল (পিডিএফ) থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
There are no exact casualty figures since 1994, but most observers agree that as many as 3,000 people, mostly soldiers, have died. Crisis Group phone interview, Jasur Sumerinli, military expert, August 2009.
- ↑ See here
- ↑ See here
- ↑ See here
- ↑ Rezvani, Babak (২০১৪)। Conflict and Peace in Central Eurasia: Towards Explanations and Understandings। Brill। পৃষ্ঠা 159। আইএসবিএন 978-9004276369।
The Karabakh conflict is an ethno-territorial conflict....
- ↑ উদ্ধৃতি ত্রুটি:
<ref>ট্যাগ বৈধ নয়;Waal_MEI2020নামের সূত্রটির জন্য কোন লেখা প্রদান করা হয়নি - ↑ "Armenia, Artsakh Security Councils hold joint session in Yerevan"। primeminister.am। The Prime Minister of the Republic of Armenia। ২৩ ডিসেম্বর ২০১৯। ৫ আগস্ট ২০২০ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
...the peaceful resolution of the Artsakh conflict.
- ↑ "Armenia-Azerbaijan Nagorno-Karabakh conflict"। nk.gov.az। Cabinet of Ministers of the Republic of Azerbaijan। ১৭ আগস্ট ২০২০ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
- ↑ "Armenia and Azerbaijan: A blockade that never ended and a peace deal hanging by a thread"। Global Voices (ইংরেজি ভাষায়)। ২০২৩-০৭-১৯। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০২৩-০৭-২৪।
- ↑ Isayev, Heydar (এপ্রিল ২০, ২০২২)। "Azerbaijan quiet as Karabakh negotiations progress"। eurasianet.org (ইংরেজি ভাষায়)। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০২৩-০১-০২।
- ↑ Vock, Ido (২০২৩-০৬-০৮)। "Fear and loathing in Armenia"। New Statesman (ইংরেজি ভাষায়)। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০২৩-০৬-০৯।
President Aliyev told Nagorno-Karabakh Armenians to 'obey the laws of Azerbaijan [and] be a loyal and normal citizen of Azerbaijan'. He threatened that if the territory’s separatist institutions were not dissolved, Azerbaijan would dissolve them by force and rejected the prospect of international protections for ethnic Armenians.
- ↑ "Armenia, Azerbaijan: Baku Launches Military Operation In Nagorno-Karabakh"। Stratfor। ২০২৩-০৯-১৯। ১৯ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০২৩-০৯-২২।
...the Russian peacekeeping contingent is incapable of preventing Azerbaijan's seizure of the region, despite this being a clear violation of the November 2020 ceasefire brokered by Russia that ended the last war.
- ↑ "Joint statement on Azerbaijan's attack on Nagorno-Karabakh | Communiqués | Documents | DSCA | Delegations | European Parliament"। www.europarl.europa.eu (ইংরেজি ভাষায়)। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০২৩-০৯-২১।
We condemn in the strongest terms today's pre-planned and unjustified attack of Azerbaijan against Nagorno-Karabakh...We recall that the attack takes place in the context of a major humanitarian crisis in Nagorno-Karabakh, following Azerbaijan's blockade of the Lachin Corridor for the past nine months, in violation of Baku's commitments under the ceasefire statement of 9 November 2020 and of the legally binding orders of the International Court of Justice. Humanitarian access to Nagorno-Karabakh needs to be fully and permanently restored.
- ↑ "Azerbaijan Launches Offensive in Breakaway Nagorno-Karabakh, Children Among Casualties"। Radiofreeeurope/Radioliberty।
- ↑ "Azerbaijani forces strike Armenian-controlled Karabakh, raising risk of new Caucasus war"। Reuters। ১৯ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩।
- ↑ "Azerbaijan launches attack in Nagorno-Karabakh, announces 'evacuation' of Armenian population"। ১৯ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩।
- ↑ "Live updates | Stepanakert under fire as Azerbaijan launches assault on Nagorno-Karabakh"। OC Media (ইংরেজি ভাষায়)। ২০২৩-০৯-১৯। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০২৩-০৯-১৯।
- ↑ "Azerbaijan says it has begun 'anti-terrorist' operations in Nagorno-Karabakh"। France 24 (ইংরেজি ভাষায়)। ২০২৩-০৯-১৯। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০২৩-০৯-১৯।
- ↑ "Russian-mediated ceasefire announced in Nagorno-Karabakh"। Armenpress।
- ↑ Tim Lister; Anna Chernova (২১ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩)। "Azerbaijan says it has retaken breakaway Armenian enclave after separatists surrender"। CNN.com।
- ↑ "Ethnic Armenians accept Russia ceasefire plan after Azerbaijan offensive in Nagorno-Karabakh"। CNN (ইংরেজি ভাষায়)। ২০ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩। ২০ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩।
- ↑ "BREAKING: Stepanakert to disband army in ceasefire deal"। CIVILNET। ২০ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩। ২০ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০ সেপ্টেম্বর ২০২৩।
- ↑ "Глава Нагорного Карабаха подписал указ о прекращении существования республики"। Коммерсантъ (রুশ ভাষায়)। ২০২৩-০৯-২৮। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০২৩-০৯-২৮।
পাদটীকা
[সম্পাদনা]- ↑ Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast (NKAO) until 1991.
- ↑ Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic (Soviet Armenia) until 1990 (renamed Republic of Armenia)/1991 (declared independence).
- ↑ Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic (Soviet Azerbaijan) until 1991.
- ↑ "Throughout the Soviet period, Moscow supported the Azerbaijani authorities against Armenian secessionists."[১] "Until the dissolution of the USSR, the Soviet authorities sided, in general, with Azerbaijan. [...] Soviet troops sent to the conflict area [...] on numerous occasions, took the side of the Azerbaijani forces to 'punish' the Armenians for raising the NK issue."[২] "Soviet troops have been in Nagorno-Karabakh for 2 1/2 years [...] The troops support armed Azerbaijani militias who have imposed a blockade of the region..."[৩] Soviet troops directly intervened during Operation Ring in April–May 1991 on the Azerbaijani side.[৪][৫] It was essentially a "combined Soviet-Azerbaijan operation."[৬]
- ↑ Armenia: 44,800 active servicemen (2019, IISS)[৩৬]
Artsakh: 18,000–20,000 active servicemen (2008, ARAG)[৩৭] - ↑ কারাবাখ সংঘাত,[৫১] আর্মেনিয়া-আজারবাইজান সংঘাত,[৫২] or Armenian–Azerbaijani conflict. Usually referred to as the Artsakh conflict in Armenia[৫৩] and the নাগর্নো-কারাবাখে আর্মেনিয়া-আজারবাইজান সংঘাত নামেও পরিচিত[৫৪]
