রোধক প্রসব: সংশোধিত সংস্করণের মধ্যে পার্থক্য
সংশোধন |
প্রলয়স্রোত (আলোচনা | অবদান) ট্যাগ: মোবাইল সম্পাদনা মোবাইল ওয়েব সম্পাদনা |
||
| ১ নং লাইন: | ১ নং লাইন: | ||
{{কাজ চলছে}} |
|||
{{Infobox medical condition (new) |
|||
| name = Obstructed labour |
|||
| synonyms = Labour dystocia |
|||
| image = Illustration of a deformed female pelvis - angular distortion Wellcome L0038229.jpg |
|||
| caption = An image of a deformed pelvis, a risk factor for obstructed labour |
|||
| field = [[Obstetrics]] |
|||
| symptoms = |
|||
| complications = [[Perinatal asphyxia]], [[uterine rupture]], [[post-partum bleeding]], [[postpartum infection]]<ref name=BMJ2003/> |
|||
| onset = |
|||
| duration = |
|||
| causes = Large or abnormally positioned baby, small [[pelvis]], problems with the birth canal<ref name=WHO2008S1/> |
|||
| risks = [[Shoulder dystocia]], [[malnutrition]], [[vitamin D deficiency]]<ref name=WHO2008S2/><ref name=WHO2008S1/> |
|||
| diagnosis = [[Active phase of labour]] > 12 hours<ref name=WHO2008S1/> |
|||
| differential = |
|||
| prevention = |
|||
| treatment = [[Cesarean section]], [[vacuum extraction]] with possible [[symphysiotomy|surgical opening of the symphysis pubis]]<ref name=WHO2008S6/> |
|||
| medication = |
|||
| prognosis = |
|||
| frequency = 6.5 million (2015)<!-- incidence table --><ref name=GBD2015Pre>{{cite journal|last1=GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence|first1=Collaborators.|title=Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015.|journal=Lancet|date=8 October 2016|volume=388|issue=10053|pages=1545–1602|pmid=27733282|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6|pmc=5055577}}</ref> |
|||
| deaths = 23,100 (2015)<ref name=GBD2015De>{{cite journal|last1=GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death|first1=Collaborators.|title=Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015.|journal=Lancet|date=8 October 2016|volume=388|issue=10053|pages=1459–1544|pmid=27733281|doi=10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1|pmc=5388903}}</ref> |
|||
}} |
|||
'''রোধক প্রসব''' বলতে সেই পরিস্থিতিকে বুঝানো হয়; যখন নবজাতক [[uterus|জরায়ুর]] স্বাভাবিক সংকোচনের ফলে যোনিপথের রুদ্ধতার দরুন শিশু ভূমিষ্ট হতে পারে না।<ref name=WHO2008S1/> এর ফলে [[Perinatal asphyxia|পর্যাপ্ত অক্সিজেন না পাওয়ার]] ফলে শিশু মারাও যেতে পারে।<ref name=BMJ2003/> এর ফলে প্রসূতি মায়ের [[puerperal infection|সংক্রমণ]], [[uterine rupture|জরায়ু বিদারণ]] অথবা [[post-partum bleeding|প্রসব পরবর্তী রক্তক্ষরণের]] ঝুঁকি বাড়তে পারে।<ref name=BMJ2003>{{cite journal|last1=Neilson|first1=JP|last2=Lavender|first2=T|last3=Quenby|first3=S|last4=Wray|first4=S|title=Obstructed labour.|journal=British Medical Bulletin|date=2003|volume=67|pages=191–204|pmid=14711764|doi=10.1093/bmb/ldg018}}</ref> [[obstetrical fistula|প্রসব জনিত ফিস্টুলার]] মত দীর্ঘস্থায়ী জটিলতা প্রজায়িনী মায়ের হতে পারে<ref name=WHO2008S1/> প্রসবকালীন সময়ে সক্রিয় পর্যায় ১২ ঘন্টার বেশি স্থায়ী হলে, [[prolonged labour|বিলম্বিত প্রসবের]] কারণে রোধক প্রসব জনিত পরিস্থিতির উদ্ভব হয়।<ref name=WHO2008S1/> |
|||
রোধক প্রসবের জন্য বেশ কিছু কারণ দায়ী। বড় অথবা অস্বাভাবিকভাবে বাচ্চার অবস্থান, ছোট [[pelvis|শ্রোণিচক্র]] এবং যোনিপথে সমস্যা রোধক প্রসবের অন্যতম কারণ।<ref name=WHO2008S1/> Abnormal positioning includes [[shoulder dystocia]] where the anterior shoulder does not pass easily below the [[pubic bone]].<ref name=WHO2008S1/> Risk factors for a small pelvis include [[malnutrition]] and a lack of exposure to sunlight causing [[vitamin D deficiency]].<ref name=WHO2008S2>{{cite book|title=Education material for teachers of midwifery : midwifery education modules|date=2008|publisher=World Health Organisation|location=Geneva [Switzerland]|isbn=9789241546669|pages=38–44|edition=2nd|url=http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2008/9789241546669_4_eng.pdf?ua=1|deadurl=no|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150221002801/http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2008/9789241546669_4_eng.pdf?ua=1|archivedate=2015-02-21|df=}}</ref> It is also more common in [[adolescence]] as the pelvis may not have finished growing.<ref name=BMJ2003/> Problems with the birth canal include a narrow vagina and perineum which may be due to [[female genital mutilation]] or [[tumors]].<ref name=WHO2008S1/> A [[partograph]] is often used to track labour progression and diagnose problems.<ref name=BMJ2003/> This combined with physical examination may identify obstructed labour.<ref name=WHO2008S3>{{cite book|title=Education material for teachers of midwifery : midwifery education modules|date=2008|publisher=World Health Organisation|location=Geneva [Switzerland]|isbn=9789241546669|pages=45–52|edition=2nd|url=http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2008/9789241546669_4_eng.pdf?ua=1|deadurl=no|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150221002801/http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2008/9789241546669_4_eng.pdf?ua=1|archivedate=2015-02-21|df=}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- Management and epidemiology--> |
|||
The treatment of obstructed labour may require [[cesarean section]] or [[vacuum extraction]] with possible [[symphysiotomy|surgical opening of the symphysis pubis]].<ref name=WHO2008S6/> Other measures include: keeping the women hydrated and [[antibiotic]]s if the [[amniotic membrane|membranes]] have been ruptured for more than 18 hours.<ref name=WHO2008S6>{{cite book|title=Education material for teachers of midwifery : midwifery education modules|date=2008|publisher=World Health Organisation|location=Geneva [Switzerland]|isbn=9789241546669|pages=89–104|edition=2nd|url=http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2008/9789241546669_4_eng.pdf?ua=1|deadurl=no|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150221002801/http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2008/9789241546669_4_eng.pdf?ua=1|archivedate=2015-02-21|df=}}</ref> In Africa and Asia obstructed labor affects between two and five percent of deliveries.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Usha|first1=Krishna|title=Pregnancy at risk : current concepts|date=2004|publisher=Jaypee Bros.|location=New Delhi|isbn=9788171798261|page=451|url=https://books.google.ca/books?id=gadYMLeYXOkC&pg=PA451|deadurl=no|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304220911/https://books.google.ca/books?id=gadYMLeYXOkC&pg=PA451|archivedate=2016-03-04|df=}}</ref> 2০১৫ সালে প্রায় ৬৫ লক্ষের মত রোধক প্রসব বা [[uterine rupture|জরায়ু বিদারণের]] মত পরিস্থিতির উদ্ভব হয়েছে<ref name=GBD2015Pre>{{cite journal|last1=GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence|first1=Collaborators.|title=Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015.|journal=Lancet|date=8 October 2016|volume=388|issue=10053|pages=1545–1602|pmid=27733282|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6|pmc=5055577}}</ref> এরফলে ২৩ হাজার নারীর মার্তৃমৃত্যু ঘটেছে। ১৯৯০ সালে ২৯০০০ মার্তৃমৃত্যু ঘটেছে (যার আট শতাংশ গর্ভাধান জনিত কারণে ঘটেছে) <ref name=WHO2008S1>{{cite book|title=Education material for teachers of midwifery : midwifery education modules|date=2008|publisher=World Health Organisation|location=Geneva [Switzerland]|isbn=9789241546669|pages=17–36|edition=2nd|url=http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2008/9789241546669_4_eng.pdf?ua=1|deadurl=no|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150221002801/http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2008/9789241546669_4_eng.pdf?ua=1|archivedate=2015-02-21|df=}}</ref><ref name=GBD2015De/><ref name=GDB2013>{{cite journal|last1=GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death|first1=Collaborators|date=17 December 2014|title=Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.|url=|journal=Lancet|volume=385|pages=117–71|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2|pmc=4340604|pmid=25530442|quote=[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4340604/bin/NIHMS61919-supplement-Supplementary_appendix.pdf |Supplementary Appendix] Page 190|via=}}</ref> [[stillbirth]] এর জন্য অন্যতম কারণ রোধক প্রসব।<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Goldenberg|first1=RL|last2=McClure|first2=EM|last3=Bhutta|first3=ZA|last4=Belizán|first4=JM|last5=Reddy|first5=UM|last6=Rubens|first6=CE|last7=Mabeya|first7=H|last8=Flenady|first8=V|last9=Darmstadt|first9=GL|last10=Lancet's Stillbirths Series steering|first10=committee.|title=Stillbirths: the vision for 2020.|journal=Lancet|date=21 May 2011|volume=377|issue=9779|pages=1798–805|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62235-0|pmid=21496912}}</ref> এধরনের পরিস্থিতি [[developing world|উন্নয়নশীল বিশ্বে]] সর্বাধিক পরিমাণে দেখা যায়।<ref name=BMJ2003/> |
|||
==মৃত্যুহার== |
==মৃত্যুহার== |
||
১৯৯০ সালে রোধক প্রসবের দরুণ মায়ের মৃত্যুর হার ছিল ২৯,০০০। ২০১৩ সালের হিসাবে এ মৃত্যুর হার ছিল ১৯,০০০।<ref name=GDB2013/> |
১৯৯০ সালে রোধক প্রসবের দরুণ মায়ের মৃত্যুর হার ছিল ২৯,০০০। ২০১৩ সালের হিসাবে এ মৃত্যুর হার ছিল ১৯,০০০।<ref name=GDB2013/> |
||
১৮:২১, ১৮ নভেম্বর ২০১৮ তারিখে সংশোধিত সংস্করণ
এই নিবন্ধ বা অনুচ্ছেদটি পরিবর্ধন বা বড় কোনো পুনর্গঠনের মধ্যে রয়েছে। এটির উন্নয়নের জন্য আপনার যে কোনো প্রকার সহায়তাকে স্বাগত জানানো হচ্ছে। যদি এই নিবন্ধ বা অনুচ্ছেদটি কয়েকদিনের জন্য সম্পাদনা করা না হয়, তাহলে অনুগ্রহপূর্বক এই টেমপ্লেটটি সরিয়ে ফেলুন। ৫ বছর আগে প্রলয়স্রোত (আলাপ | অবদান) এই নিবন্ধটি সর্বশেষ সম্পাদনা করেছেন। (হালনাগাদ) |
| Obstructed labour | |
|---|---|
| প্রতিশব্দ | Labour dystocia |
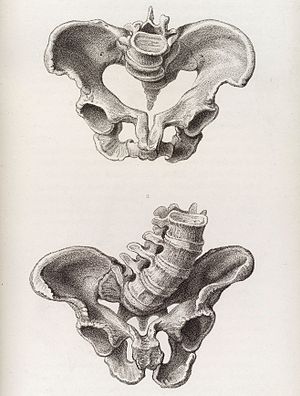 | |
| An image of a deformed pelvis, a risk factor for obstructed labour | |
| বিশেষত্ব | Obstetrics |
| জটিলতা | Perinatal asphyxia, uterine rupture, post-partum bleeding, postpartum infection[১] |
| কারণ | Large or abnormally positioned baby, small pelvis, problems with the birth canal[২] |
| ঝুঁকির কারণ | Shoulder dystocia, malnutrition, vitamin D deficiency[৩][২] |
| রোগনির্ণয়ের পদ্ধতি | Active phase of labour > 12 hours[২] |
| চিকিৎসা | Cesarean section, vacuum extraction with possible surgical opening of the symphysis pubis[৪] |
| সংঘটনের হার | 6.5 million (2015)[৫] |
| মৃতের সংখ্যা | 23,100 (2015)[৬] |
রোধক প্রসব বলতে সেই পরিস্থিতিকে বুঝানো হয়; যখন নবজাতক জরায়ুর স্বাভাবিক সংকোচনের ফলে যোনিপথের রুদ্ধতার দরুন শিশু ভূমিষ্ট হতে পারে না।[২] এর ফলে পর্যাপ্ত অক্সিজেন না পাওয়ার ফলে শিশু মারাও যেতে পারে।[১] এর ফলে প্রসূতি মায়ের সংক্রমণ, জরায়ু বিদারণ অথবা প্রসব পরবর্তী রক্তক্ষরণের ঝুঁকি বাড়তে পারে।[১] প্রসব জনিত ফিস্টুলার মত দীর্ঘস্থায়ী জটিলতা প্রজায়িনী মায়ের হতে পারে[২] প্রসবকালীন সময়ে সক্রিয় পর্যায় ১২ ঘন্টার বেশি স্থায়ী হলে, বিলম্বিত প্রসবের কারণে রোধক প্রসব জনিত পরিস্থিতির উদ্ভব হয়।[২]
রোধক প্রসবের জন্য বেশ কিছু কারণ দায়ী। বড় অথবা অস্বাভাবিকভাবে বাচ্চার অবস্থান, ছোট শ্রোণিচক্র এবং যোনিপথে সমস্যা রোধক প্রসবের অন্যতম কারণ।[২] Abnormal positioning includes shoulder dystocia where the anterior shoulder does not pass easily below the pubic bone.[২] Risk factors for a small pelvis include malnutrition and a lack of exposure to sunlight causing vitamin D deficiency.[৩] It is also more common in adolescence as the pelvis may not have finished growing.[১] Problems with the birth canal include a narrow vagina and perineum which may be due to female genital mutilation or tumors.[২] A partograph is often used to track labour progression and diagnose problems.[১] This combined with physical examination may identify obstructed labour.[৭]
The treatment of obstructed labour may require cesarean section or vacuum extraction with possible surgical opening of the symphysis pubis.[৪] Other measures include: keeping the women hydrated and antibiotics if the membranes have been ruptured for more than 18 hours.[৪] In Africa and Asia obstructed labor affects between two and five percent of deliveries.[৮] 2০১৫ সালে প্রায় ৬৫ লক্ষের মত রোধক প্রসব বা জরায়ু বিদারণের মত পরিস্থিতির উদ্ভব হয়েছে[৫] এরফলে ২৩ হাজার নারীর মার্তৃমৃত্যু ঘটেছে। ১৯৯০ সালে ২৯০০০ মার্তৃমৃত্যু ঘটেছে (যার আট শতাংশ গর্ভাধান জনিত কারণে ঘটেছে) [২][৬][৯] stillbirth এর জন্য অন্যতম কারণ রোধক প্রসব।[১০] এধরনের পরিস্থিতি উন্নয়নশীল বিশ্বে সর্বাধিক পরিমাণে দেখা যায়।[১]
মৃত্যুহার
১৯৯০ সালে রোধক প্রসবের দরুণ মায়ের মৃত্যুর হার ছিল ২৯,০০০। ২০১৩ সালের হিসাবে এ মৃত্যুর হার ছিল ১৯,০০০।[৯]
আরো পড়ুন
টেমপ্লেট:চিকিৎসার অবস্থার প্রকারভেদ এবং সম্পদ
- Education material for teachers of midwifery : midwifery education modules (পিডিএফ) (2nd সংস্করণ)। Geneva [Switzerland]: World Health Organisation। ২০০৮। আইএসবিএন 9789241546669।
টেমপ্লেট:গর্ভবস্থার রোগবিদ্যা,প্রসবাবস্থা এবং puerperium
- ↑ ক খ গ ঘ ঙ চ Neilson, JP; Lavender, T; Quenby, S; Wray, S (২০০৩)। "Obstructed labour."। British Medical Bulletin। 67: 191–204। ডিওআই:10.1093/bmb/ldg018। পিএমআইডি 14711764।
- ↑ ক খ গ ঘ ঙ চ ছ জ ঝ ঞ Education material for teachers of midwifery : midwifery education modules (পিডিএফ) (2nd সংস্করণ)। Geneva [Switzerland]: World Health Organisation। ২০০৮। পৃষ্ঠা 17–36। আইএসবিএন 9789241546669। ২০১৫-০২-২১ তারিখে মূল (পিডিএফ) থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
- ↑ ক খ Education material for teachers of midwifery : midwifery education modules (পিডিএফ) (2nd সংস্করণ)। Geneva [Switzerland]: World Health Organisation। ২০০৮। পৃষ্ঠা 38–44। আইএসবিএন 9789241546669। ২০১৫-০২-২১ তারিখে মূল (পিডিএফ) থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
- ↑ ক খ গ Education material for teachers of midwifery : midwifery education modules (পিডিএফ) (2nd সংস্করণ)। Geneva [Switzerland]: World Health Organisation। ২০০৮। পৃষ্ঠা 89–104। আইএসবিএন 9789241546669। ২০১৫-০২-২১ তারিখে মূল (পিডিএফ) থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
- ↑ ক খ GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence, Collaborators. (৮ অক্টোবর ২০১৬)। "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015."। Lancet। 388 (10053): 1545–1602। ডিওআই:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6। পিএমআইডি 27733282। পিএমসি 5055577
 ।
।
- ↑ ক খ GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators. (৮ অক্টোবর ২০১৬)। "Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015."। Lancet। 388 (10053): 1459–1544। ডিওআই:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1। পিএমআইডি 27733281। পিএমসি 5388903
 ।
।
- ↑ Education material for teachers of midwifery : midwifery education modules (পিডিএফ) (2nd সংস্করণ)। Geneva [Switzerland]: World Health Organisation। ২০০৮। পৃষ্ঠা 45–52। আইএসবিএন 9789241546669। ২০১৫-০২-২১ তারিখে মূল (পিডিএফ) থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
- ↑ Usha, Krishna (২০০৪)। Pregnancy at risk : current concepts। New Delhi: Jaypee Bros.। পৃষ্ঠা 451। আইএসবিএন 9788171798261। ২০১৬-০৩-০৪ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
- ↑ ক খ GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators (১৭ ডিসেম্বর ২০১৪)। "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013."। Lancet। 385: 117–71। ডিওআই:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2। পিএমআইডি 25530442। পিএমসি 4340604
 ।
। |Supplementary Appendix Page 190
- ↑ Goldenberg, RL; McClure, EM; Bhutta, ZA; Belizán, JM; Reddy, UM; Rubens, CE; Mabeya, H; Flenady, V; Darmstadt, GL; Lancet's Stillbirths Series steering, committee. (২১ মে ২০১১)। "Stillbirths: the vision for 2020."। Lancet। 377 (9779): 1798–805। ডিওআই:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62235-0। পিএমআইডি 21496912।
