প্যারাসিটামল: সংশোধিত সংস্করণের মধ্যে পার্থক্য
সম্পাদনা সারাংশ নেই ট্যাগ: মোবাইল সম্পাদনা মোবাইল ওয়েব সম্পাদনা |
ছক ট্যাগ: মোবাইল সম্পাদনা মোবাইল ওয়েব সম্পাদনা |
||
| ১ নং লাইন: | ১ নং লাইন: | ||
{{drugbox |
{{drugbox |
||
| Watchedfields = changed |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| verifiedrevid = 456349142 |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
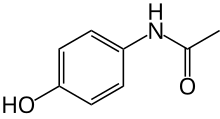
| image = Paracetamol-skeletal.svg |
| image = Paracetamol-skeletal.svg |
||
| image2= Paracetamol-from-xtal-3D-balls.png |
| image2 = Paracetamol-from-xtal-3D-balls.png |
||
| |
| drug_name = |
||
| USAN=acetaminophen |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
<!--Clinical data--> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
|synonyms = N-acetyl-para-aminophenol (APAP) |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| pronounce = প্যারাসিটামল {{IPAc-en|ˌ|p|ær|ə|ˈ|s|iː|t|ə|m|ɒ|l}}<br />অ্যাসিটামিনোফেন: {{IPAc-en|audio=Acetaminophen.ogg|ə|ˌ|s|iː|t|ə|ˈ|m|ɪ|n|ə|f|ᵻ|n}} |
|||
| tradename = [[Tylenol (brand)|টাইনেলন]], [[Panadol (brand)|প্যামাডল]], [[list of paracetamol brand names|অন্যান্য]]<ref name=drugs.com-internatl>{{ওয়েব উদ্ধৃতি|title=International Listings for Paracetamol|url=https://www.drugs.com/international/paracetamol.html|accessdate=11 January 2016|deadurl=no|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20160106130210/http://www.drugs.com/international/paracetamol.html|archivedate=6 January 2016|df=}}</ref> |
|||
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|monograph|acetaminophen}} |
|||
| MedlinePlus = a681004 |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
|pregnancy_US_comment=<ref name=AHFS2016/> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| routes_of_administration = [[Oral administration|মুখ দ্বারা]], [[Buccal administration|গাল দ্বারা]], [[rectal administration|পায়ু দ্বারা]], [[Intravenous administration|intravenous]] (IV) |
|||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> |
|||
| ⚫ | | bioavailability = 63–89%<ref>{{বই উদ্ধৃতি|isbn=9780977517459 |title=Acute Pain Management: Scientific Evidence |author=Working Group of the Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists and Faculty of Pain Medicine |year=2010 |publisher=National Health and Medical Research Council |location=Melbourne, Australia |url=http://www.anzca.edu.au/resources/college-publications/pdfs/Acute%20Pain%20Management/books-and-publications/acutepain.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121021093616/http://www.anzca.edu.au/resources/college-publications/pdfs/Acute%20Pain%20Management/books-and-publications/acutepain.pdf |dead-url=yes |archive-date=2012-10-21 |format=PDF |edition=3rd |editor1=Macintyre, PE |editor2=Schug, SA |editor3=Scott, DA |editor4=Visser, EJ |editor5=Walker, SM |df= }}</ref>{{rp|73}} |
||
| protein_bound = ১০–২৫%<ref>{{ওয়েব উদ্ধৃতি|title=Tylenol, Tylenol Infants' Drops (acetaminophen) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more|work=Medscape Reference|publisher=WebMD|accessdate=10 May 2014|url=http://reference.medscape.com/drug/tylenol-acetaminophen-343346#showall|deadurl=no|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20140414025534/http://reference.medscape.com/drug/tylenol-acetaminophen-343346#showall|archivedate=14 April 2014|df=}}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | | metabolism = Predominantly in the liver<ref name = TGA>{{cite web|title=Codapane Forte Paracetamol and codeine phosphate PRODUCT INFORMATION|work=TGA eBusiness Services|publisher=Alphapharm Pty Limited|date=29 April 2013|accessdate=10 May 2014 |url=https://www.ebs.tga.gov.au/ebs/picmi/picmirepository.nsf/pdf?OpenAgent&id=CP-2010-PI-05623-3|format=PDF}}</ref> |
||
| metabolites = APAP [[Glucuronide|gluc]], APAP [[sulfate]], APAP [[Glutathione|GSH]], APAP [[cys]], [[NAPQI]]<ref>{{cite web |title= Acetaminophen Pathway (therapeutic doses), Pharmacokinetics |accessdate= 13 January 2016 |url= https://www.pharmgkb.org/pathway/PA165986279 |deadurl= no |archiveurl= https://web.archive.org/web/20160304220600/https://www.pharmgkb.org/pathway/PA165986279 |archivedate= 4 March 2016 |df= }}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| onset = Pain relief onset by [[Route of administration|route]]:<br />[[Oral administration|By mouth]] – 37 minutes<ref name="Buccal route">{{সাময়িকী উদ্ধৃতি| vauthors = Pickering G, Macian N, Libert F, Cardot JM, Coissard S, Perovitch P, Maury M, Dubray C | title = Buccal acetaminophen provides fast analgesia: two randomized clinical trials in healthy volunteers | journal = Drug Des. Devel. Ther. | volume = 8 | issue = | pages = 1621–1627 | date = September 2014 | pmid = 25302017 | pmc = 4189711 | doi = 10.2147/DDDT.S63476 | quote = bAPAP has a faster time of antinociception onset (15 minutes, P<0.01) and greater antinociception at 50 minutes (P<0.01, CT1) and 30 minutes (P<0.01, CT2) than ivAPAP and sAPAP. All routes are similar after 50 minutes. ... In postoperative conditions for acute pain of mild to moderate intensity, the quickest reported time to onset of analgesia with APAP is 8 minutes9 for the iv route and 37 minutes6 for the oral route.}}</ref><br />[[Buccal administration|Buccal]] – ১৫ মিনিট<ref name="Buccal route" /><br />[[Intravenous]] – 8 minutes<ref name="Buccal route" /> |
|||
<!--Identifiers--> |
|||
| IUPHAR_ligand = 5239 |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| CAS_number = 103-90-2 |
|||
| ATC_prefix = N02 |
| ATC_prefix = N02 |
||
| ATC_suffix = BE01 |
| ATC_suffix = BE01 |
||
| PubChem = 1983 |
| PubChem = 1983 |
||
| smiles = C1=CC(=CC=C1NC(C)=O)O |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} |
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} |
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} |
||
| UNII = 362O9ITL9D |
| UNII = 362O9ITL9D |
||
| ২২ নং লাইন: | ৫২ নং লাইন: | ||
| ChEMBL = 112 |
| ChEMBL = 112 |
||
| PDB_ligand = TYL |
| PDB_ligand = TYL |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
<!-- |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| pKa = 9.5 |
|||
| solubility = 14 mg/mL @ 25C |
|||
--> |
|||
| ⚫ | | bioavailability = 63–89%<ref>{{বই উদ্ধৃতি |
||
| ⚫ | | metabolism = |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| routes_of_administration = [[Oral]], [[rectal]], [[Intravenous therapy|intravenous]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
}} |
|||
<!--Chemical data--> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| SMILES = CC(=O)Nc1ccc(O)cc1 |
|||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
|||
| StdInChI = 1S/C8H9NO2/c1-6(10)9-7-2-4-8(11)5-3-7/h2-5,11H,1H3,(H,9,10) |
|||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
|||
| StdInChIKey = RZVAJINKPMORJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| melting_point = 169 |
|||
| boiling_point = 420 |
|||
| ⚫ | | melting_notes =<ref>{{Cite journal | doi = 10.1021/ci0500132 | title = General Melting Point Prediction Based on a Diverse Compound Data Set and Artificial Neural Networks | year = 2005 | last1 = Karthikeyan | first1 = M. | last2 = Glen | first2 = R. C. | last3 = Bender | first3 = A. | journal = Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling | volume = 45 | issue = 3 | pages = 581–590 | pmid = 15921448}}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url = http://lxsrv7.oru.edu/~alang/meltingpoints/meltingpointof.php?csid=1906 | title = melting point data for paracetamol | publisher = Lxsrv7.oru.edu | accessdate = 19 March 2011 | deadurl = yes | archiveurl = https://archive.is/20120630213835/http://lxsrv7.oru.edu/~alang/meltingpoints/meltingpointof.php?csid=1906 | archivedate = 30 June 2012 | df = }}</ref> |
||
| solubility = 7.21 g/kg (0 °C)<ref name="paracetamol-solubility">{{cite journal | doi = 10.1021/je990124v | title = Solubility of paracetamol in pure solvents |vauthors=Granberg RA, Rasmuson AC | journal = [[Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data]] | volume = 44 | issue = 6 | pages = 1391–95 | year = 1999}}</ref><br /> |
|||
8.21 g/kg (5°C)<ref name="paracetamol-solubility" /><br /> |
|||
9.44 g/kg (10°C)<ref name="paracetamol-solubility" /><br /> |
|||
10.97 g/kg (15°C)<ref name="paracetamol-solubility" /><br /> |
|||
12.78 g/kg (20°C)<ref name="paracetamol-solubility" /><br /> |
|||
~14<!-- mg/ml (20°C) is appended--> |
|||
|caption= |
|||
<!-- this is class not type: |type=non steroidal anti infalmatory drug (NSAIDs) --> |
|||
|legal_status= |
|||
|licence_EU=|alt=|type=}} |
|||
'''প্যারাসিটামল''' একটি সুলভ ঔষধ যা সচরাচর জ্বর ও ব্যথা উপশমে সেবন করা হয়। এটি যুগপৎ "অ্যানালজেসিক" এবং "অ্যান্টিপাইরেটিক" শ্রেণীর ঔষধ; পানিতে সহজে দ্রবণীয়। এর অন্য নাম অ্যাসিটামিনোফেন (acetaminophen )। |
'''প্যারাসিটামল''' একটি সুলভ ঔষধ যা সচরাচর জ্বর ও ব্যথা উপশমে সেবন করা হয়। এটি যুগপৎ "অ্যানালজেসিক" এবং "অ্যান্টিপাইরেটিক" শ্রেণীর ঔষধ; পানিতে সহজে দ্রবণীয়। এর অন্য নাম অ্যাসিটামিনোফেন (acetaminophen )। |
||
১০:৩০, ১৪ নভেম্বর ২০১৮ তারিখে সংশোধিত সংস্করণ
 | |
 | |
| রোগশয্যাসম্বন্ধীয় তথ্য | |
|---|---|
| উচ্চারণ | প্যারাসিটামল /ˌpærəˈsiːtəmɒl/ অ্যাসিটামিনোফেন: /əˌsiːtəˈmɪnəfɪn/ (ⓘ) |
| বাণিজ্যিক নাম | টাইনেলন, প্যামাডল, অন্যান্য[২] |
| অন্যান্য নাম | টেমপ্লেট:Infobox drug/localINNvariants |
| এএইচএফএস/ ড্রাগস.কম | মনোগ্রাফ |
| মেডলাইনপ্লাস | a681004 |
| লাইসেন্স উপাত্ত |
|
| গর্ভাবস্থার শ্রেণি |
|
| প্রয়োগের স্থান | মুখ দ্বারা, গাল দ্বারা, পায়ু দ্বারা, intravenous (IV) |
| এটিসি কোড | |
| আইনি অবস্থা | |
| আইনি অবস্থা |
|
| ফার্মাকোকাইনেটিক উপাত্ত | |
| জৈবপ্রাপ্যতা | 63–89%[৪]:৭৩ |
| প্রোটিন বন্ধন | ১০–২৫%[৫] |
| বিপাক | Predominantly in the liver[৩] |
| মেটাবলাইট | APAP gluc, APAP sulfate, APAP GSH, APAP cys, NAPQI[৬] |
| কর্মের সূত্রপাত | Pain relief onset by route: By mouth – 37 minutes[৭] Buccal – ১৫ মিনিট[৭] Intravenous – 8 minutes[৭] |
| বর্জন অর্ধ-জীবন | ১–৪ hours[৩] |
| রেচন | মুত্র (85–90%)[৩] |
| শনাক্তকারী | |
| |
| সিএএস নম্বর | |
| পাবকেম সিআইডি | |
| আইইউপিএইচএআর/ বিপিএস | |
| ড্রাগব্যাংক | |
| কেমস্পাইডার | |
| ইউএনআইআই | |
| কেইজিজি | |
| সিএইচইবিআই | |
| সিএইচইএমবিএল | |
| পিডিবি লিগ্যান্ড | |
| কমপটক্স ড্যাশবোর্ড (আইপিএ) | |
| ইসিএইচএ ইনফোকার্ড | 100.002.870 |
| রাসায়নিক ও ভৌত তথ্য | |
| সংকেত | C8H9NO2 |
| মোলার ভর | 151.163 g/mol |
| থ্রিডি মডেল (জেএসমোল) | |
| ঘনত্ব | 1.263 g/cm3 |
| গলনাঙ্ক | ১৬৯ °সে (৩৩৬ °ফা) [৯][১০] |
| স্ফুটনাংক | ৪২০ °সে (৭৮৮ °ফা) |
| জলে দ্রাব্যতা | 7.21 g/kg (0 °C)[৮] 8.21 g/kg (5°C)[৮] |
| |
| |
প্যারাসিটামল একটি সুলভ ঔষধ যা সচরাচর জ্বর ও ব্যথা উপশমে সেবন করা হয়। এটি যুগপৎ "অ্যানালজেসিক" এবং "অ্যান্টিপাইরেটিক" শ্রেণীর ঔষধ; পানিতে সহজে দ্রবণীয়। এর অন্য নাম অ্যাসিটামিনোফেন (acetaminophen )।
প্যারাসিটামল একটি জেনেরিক নাম এবং বিভিন্ন ঔষধ প্রস্তুতকারক প্রতিষ্ঠান রুচিমাফিক নানা নামে প্যারাসিটামল উৎপাদন ও বাজারজাত করে।প্যারাসিটামল আবিষ্কার হয় ১৮৭৭ সালে।[১১]
এটি দৈনিক সর্বোচ্চ 4000 mg (৪ গ্রাম) পর্যন্ত গ্রহণ করা যায়। সাধারণত ৫০০ মিলিগ্রামের ট্যাবলেট বা ক্যাপলেট আকারে এটি বাজারজাত করা হয়। প্রাপ্ত বয়স্ক ব্যক্তির জন্য সর্বোচ্চ হার প্রতি বারে ১০০০ মিলিগ্রাম। প্যারাসিটামল একটি "ওভার দি কাউন্টার মেডিসিন" অর্থাৎ ডাক্তারের চিকিৎসাপত্র ব্যাতিরেকেই এটি কিনতে পাওয়া যায়। তাই অনেকে যখন-তখন অর্থাৎ সামান্য উপসর্গে প্যারাসিটামল গ্রহণ করে। সাধারণভাবে পার্শ্বপ্রতিক্রিয়াহীন হলেও অধিক ব্যবহার যকৃতের জন্য ক্ষতিকর। এমনকি লিভার সিরোসিসও হতে পারে। অ্যাসিটামিনোফেনে যাদের অ্যালার্জি আছে তাদের এই ঔষধ গ্রহণ করা ঠিক নয়। কিডনীর সমস্যা থাকলে বা মাদকাসক্ত থাকলে ডাক্তারের পরামর্শ ব্যাতিরেকে প্যারাসিটামল সেবন করা নিষেধ।
এটি ট্যাবলেট, সিরাপ, সাসপেনশন ও সাপোজিটর ফর্মে পাওয়া যায়। অনেক ক্ষেত্রে প্যারাসিটামলের সঙ্গে ক্যাফেইন মিশিয়ে প্যারাসিটামল ট্যাবলেট প্রস্তুত করা হয়। এতে ব্যথানাশক ক্রিয়া বৃদ্ধি পায় অর্থাৎ ব্যথা নিরাময়ে দ্রুততর কাজ করে।
তথ্যসূত্র
- ↑ উদ্ধৃতি ত্রুটি:
<ref>ট্যাগ বৈধ নয়;AHFS2016নামের সূত্রটির জন্য কোন লেখা প্রদান করা হয়নি - ↑ "International Listings for Paracetamol"। ৬ জানুয়ারি ২০১৬ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১১ জানুয়ারি ২০১৬।
- ↑ ক খ গ "Codapane Forte Paracetamol and codeine phosphate PRODUCT INFORMATION" (PDF)। TGA eBusiness Services। Alphapharm Pty Limited। ২৯ এপ্রিল ২০১৩। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১০ মে ২০১৪।
- ↑ Working Group of the Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists and Faculty of Pain Medicine (২০১০)। Macintyre, PE; Schug, SA; Scott, DA; Visser, EJ; Walker, SM, সম্পাদকগণ। Acute Pain Management: Scientific Evidence (পিডিএফ) (3rd সংস্করণ)। Melbourne, Australia: National Health and Medical Research Council। আইএসবিএন 9780977517459। ২০১২-১০-২১ তারিখে মূল (PDF) থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
- ↑ "Tylenol, Tylenol Infants' Drops (acetaminophen) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more"। Medscape Reference। WebMD। ১৪ এপ্রিল ২০১৪ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১০ মে ২০১৪।
- ↑ "Acetaminophen Pathway (therapeutic doses), Pharmacokinetics"। ৪ মার্চ ২০১৬ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১৩ জানুয়ারি ২০১৬।
- ↑ ক খ গ Pickering G, Macian N, Libert F, Cardot JM, Coissard S, Perovitch P, Maury M, Dubray C (সেপ্টেম্বর ২০১৪)। "Buccal acetaminophen provides fast analgesia: two randomized clinical trials in healthy volunteers"। Drug Des. Devel. Ther.। 8: 1621–1627। ডিওআই:10.2147/DDDT.S63476। পিএমআইডি 25302017। পিএমসি 4189711
 ।
। bAPAP has a faster time of antinociception onset (15 minutes, P<0.01) and greater antinociception at 50 minutes (P<0.01, CT1) and 30 minutes (P<0.01, CT2) than ivAPAP and sAPAP. All routes are similar after 50 minutes. ... In postoperative conditions for acute pain of mild to moderate intensity, the quickest reported time to onset of analgesia with APAP is 8 minutes9 for the iv route and 37 minutes6 for the oral route.
- ↑ ক খ গ ঘ ঙ Granberg RA, Rasmuson AC (১৯৯৯)। "Solubility of paracetamol in pure solvents"। Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data। 44 (6): 1391–95। ডিওআই:10.1021/je990124v।
- ↑ Karthikeyan, M.; Glen, R. C.; Bender, A. (২০০৫)। "General Melting Point Prediction Based on a Diverse Compound Data Set and Artificial Neural Networks"। Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling। 45 (3): 581–590। ডিওআই:10.1021/ci0500132। পিএমআইডি 15921448।
- ↑ "melting point data for paracetamol"। Lxsrv7.oru.edu। ৩০ জুন ২০১২ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১৯ মার্চ ২০১১।
- ↑ Mangus, Brent C.; Miller, Michael G. (২০০৫)। Pharmacology application in athletic training। Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: F.A. Davis। পৃষ্ঠা 39। আইএসবিএন 9780803620278।
বহিঃসংযোগ
- Paracetamol at Chemsynthesis
- Paracetamol Information Centre
- Paracetamol International Chemical Safety Cards
- The Julius Axelrod Papers
- FDA: Safe Use of Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers/Fever Reducers
- FDA: Consumer Update "Acetaminophen and Liver Injury: Q and A for Consumers" (link)
- FDA: Consumer Update "Acetaminophen and Liver Injury: Q and A for Consumers" (PDF)
- U.S. National Library of Medicine: Drug Information Portal–Paracetamol
- Acetaminophen bound to proteins in the Protein Data Bank
