হিন্দু-আরবি সংখ্যা পদ্ধতি: সংশোধিত সংস্করণের মধ্যে পার্থক্য
অ Added {{lead too short}} and {{unreferenced}} tags to article (TW) |
সম্প্রসারণ |
||
| ১ নং লাইন: | ১ নং লাইন: | ||
{{lead too short|date=মার্চ ২০১৪}} |
|||
{{unreferenced|date=মার্চ ২০১৪}} |
|||
[[Image:Arabic Numerals.svg|thumb|300px|right|আরবি সংখ্যা পদ্ধতি]] |
[[Image:Arabic Numerals.svg|thumb|300px|right|আরবি সংখ্যা পদ্ধতি]] |
||
'''আরবি সংখ্যা পদ্ধতি''' বিশ্বের সবচেয়ে বেশি ব্যবহাত সংখ্যা পদ্ধতি। এর ব্যবহার অনেক ভাষায় দেখা যায়। |
'''আরবি সংখ্যা পদ্ধতি''' বিশ্বের সবচেয়ে বেশি ব্যবহাত সংখ্যা পদ্ধতি। এর ব্যবহার অনেক ভাষায় দেখা যায়। পদ্ধতিটিতে দশটি অঙ্ক আছে: ০, ১, ২, ৩, ৪, ৫, ৬, ৭, ৮ এবং ৯। এ পদ্ধতিতে একাধিক অঙ্ককে পাশাপাশি বসিয়ে একটি মাত্র সংখ্যা হিসেবে পড়া হয়। সংখ্যাটিতে অঙ্কের অবস্থান অনুযায়ী সেটির মান নিরূপণ করা হয়। শূন্যের প্রতীক পদ্ধতিটির সাফল্যের চাবিকাঠি। ৫০০ খ্রিস্টাব্দের দিকে ভারতীয় উপমহাদেশের গণিতবিদেরা পদ্ধতিটি উদ্ভাবন করেন।<ref name="Cengage Learning"> |
||
{{cite book |
|||
| first1=Richard |last1= Bulliet|first2= Pamela |last2=Crossley|first3= Daniel |last3=Headrick,|first4= Steven |last4= Hirsch|first5= Lyman |last5= Johnson |
|||
| title = The Earth and Its Peoples: A Global History, Volume 1 |
|||
|page = 192 |
|||
|quote = Indian mathematicians invented the concept of zero and developed the "Arabic" numerals and system of place-value notation used in most parts of the world today |
|||
|publisher = Cengage Learning |
|||
|year = 2010 |
|||
|url = https://books.google.com/books?id=dOxl71w-jHEC&pg=PA192 |
|||
|isbn = 1439084742}} |
|||
</ref> এ কারণে এটিকে '''হিন্দু-আরবি সংখ্যা পদ্ধতি'''<ref name="HA"> |
|||
{{Citation | last1 = Schipp| first1 = Bernhard| last2 = Krämer| first2 = Walter| title = Statistical Inference, Econometric Analysis and Matrix Algebra: Festschrift in Honour of Götz Trenkler| publisher = [[Springer Science+Business Media|Springer]]| year = 2008| page = 387| url = https://books.google.com/?id=t6XfLJzqO_kC&pg=PA387| isbn = 9783790821208}} |
|||
</ref><ref> |
|||
{{Citation | last1 = Lumpkin| first1 = Beatrice| last2 = Strong| first2 = Dorothy| title = Multicultural science and math connections: middle school projects and activities| publisher = Walch Publishing| year = 1995| page = 118| url = https://books.google.com/?id=2LgG8lsJQmAC&pg=PA118| isbn = 9780825126598}} |
|||
</ref> বা '''হিন্দু সংখ্যা পদ্ধতি'''ও<ref> |
|||
{{cite book|last=Downey|first=Tika|title=The History of Zero: Exploring Our Place-Value Number System|year=2004|isbn=978-0823988693 |pages=22}}; |
|||
''"Fibonacci recognized that the Hindu numerals had many advantages-over the Roman numerals that were then used in Europe. The 4 basic math operations — addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division could all be performed much more easily with Hindu numerals than with Roman Numerals."'' |
|||
</ref> বলা হয়। মধ্যপ্রাচ্যে প্রথমে বাগদাদের গণিতবিদেরা সংখ্যা পদ্ধতিটি গ্রহণ করেন এবং আরও পশ্চিমের আরবদের কাছে এটিকে ছড়িয়ে দেন। উত্তর আফ্রিকার বেজাইয়া শহরে ইতালীয় পণ্ডিত ফিবোনাচ্চি প্রথম এই সংখ্যা পদ্ধতির সাথে পরিচিত হন। তাঁর কাজের মাধ্যমে সমস্ত ইউরোপ পদ্ধতিটির সাথে পরিচিত হয়। |
|||
==তথ্যসূত্র== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{সূত্র তালিকা}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
০৫:০৪, ১৩ ডিসেম্বর ২০১৬ তারিখে সংশোধিত সংস্করণ
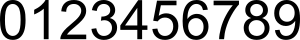
আরবি সংখ্যা পদ্ধতি বিশ্বের সবচেয়ে বেশি ব্যবহাত সংখ্যা পদ্ধতি। এর ব্যবহার অনেক ভাষায় দেখা যায়। পদ্ধতিটিতে দশটি অঙ্ক আছে: ০, ১, ২, ৩, ৪, ৫, ৬, ৭, ৮ এবং ৯। এ পদ্ধতিতে একাধিক অঙ্ককে পাশাপাশি বসিয়ে একটি মাত্র সংখ্যা হিসেবে পড়া হয়। সংখ্যাটিতে অঙ্কের অবস্থান অনুযায়ী সেটির মান নিরূপণ করা হয়। শূন্যের প্রতীক পদ্ধতিটির সাফল্যের চাবিকাঠি। ৫০০ খ্রিস্টাব্দের দিকে ভারতীয় উপমহাদেশের গণিতবিদেরা পদ্ধতিটি উদ্ভাবন করেন।[১] এ কারণে এটিকে হিন্দু-আরবি সংখ্যা পদ্ধতি[২][৩] বা হিন্দু সংখ্যা পদ্ধতিও[৪] বলা হয়। মধ্যপ্রাচ্যে প্রথমে বাগদাদের গণিতবিদেরা সংখ্যা পদ্ধতিটি গ্রহণ করেন এবং আরও পশ্চিমের আরবদের কাছে এটিকে ছড়িয়ে দেন। উত্তর আফ্রিকার বেজাইয়া শহরে ইতালীয় পণ্ডিত ফিবোনাচ্চি প্রথম এই সংখ্যা পদ্ধতির সাথে পরিচিত হন। তাঁর কাজের মাধ্যমে সমস্ত ইউরোপ পদ্ধতিটির সাথে পরিচিত হয়।
তথ্যসূত্র
- ↑
Bulliet, Richard; Crossley, Pamela; Headrick,, Daniel; Hirsch, Steven; Johnson, Lyman (২০১০)। The Earth and Its Peoples: A Global History, Volume 1। Cengage Learning। পৃষ্ঠা 192। আইএসবিএন 1439084742।
Indian mathematicians invented the concept of zero and developed the "Arabic" numerals and system of place-value notation used in most parts of the world today
- ↑ Schipp, Bernhard; Krämer, Walter (২০০৮), Statistical Inference, Econometric Analysis and Matrix Algebra: Festschrift in Honour of Götz Trenkler, Springer, পৃষ্ঠা 387, আইএসবিএন 9783790821208
- ↑ Lumpkin, Beatrice; Strong, Dorothy (১৯৯৫), Multicultural science and math connections: middle school projects and activities, Walch Publishing, পৃষ্ঠা 118, আইএসবিএন 9780825126598
- ↑ Downey, Tika (২০০৪)। The History of Zero: Exploring Our Place-Value Number System। পৃষ্ঠা 22। আইএসবিএন 978-0823988693।; "Fibonacci recognized that the Hindu numerals had many advantages-over the Roman numerals that were then used in Europe. The 4 basic math operations — addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division could all be performed much more easily with Hindu numerals than with Roman Numerals."
