নাৎসি বাহিনীর পোল্যান্ড আক্রমণ: সংশোধিত সংস্করণের মধ্যে পার্থক্য
অ Removing Link GA template (handled by wikidata) |
অ আইএসবিএন টেমপ্লেট যোগ |
||
| ৩৩ নং লাইন: | ৩৩ নং লাইন: | ||
Equipment losses are given as 832 German tanks <ref name="ReferenceC"> |
Equipment losses are given as 832 German tanks <ref name="ReferenceC"> |
||
KAMIL CYWINSKI, ''Waffen und Geheimwaffen des deutschen Heeres 1933-1945''</ref> of with approximately 236<ref name="ReferenceC"/> to 341 as irrecoverable losses and approximately 319 other armoured vehicles as irrecoverable losses (including 165 Panzer Spahwagen – of them 101 as irrecoverable losses)<ref name="ReferenceC"/> 522–561 German planes (including 246–285 destroyed and 276 damaged), 1 German minelayer (M-85) and 1 German torpedo ship ("Tiger")|group="Note"}}<br />16,343 killed,<br />3,500 missing,<ref>[http://books.google.ca/books?id=gLE9AAAAIAAJ&pg=PA133&dq=%2230,300+wounded+and+about+3,500+missing%22&cd=1#v=onepage&q=%2230%2C300%20wounded%20and%20about%203%2C500%20missing%22&f=false The encyclopedia of modern war By Roger Parkinson] Taylor & Francis, |
KAMIL CYWINSKI, ''Waffen und Geheimwaffen des deutschen Heeres 1933-1945''</ref> of with approximately 236<ref name="ReferenceC"/> to 341 as irrecoverable losses and approximately 319 other armoured vehicles as irrecoverable losses (including 165 Panzer Spahwagen – of them 101 as irrecoverable losses)<ref name="ReferenceC"/> 522–561 German planes (including 246–285 destroyed and 276 damaged), 1 German minelayer (M-85) and 1 German torpedo ship ("Tiger")|group="Note"}}<br />16,343 killed,<br />3,500 missing,<ref>[http://books.google.ca/books?id=gLE9AAAAIAAJ&pg=PA133&dq=%2230,300+wounded+and+about+3,500+missing%22&cd=1#v=onepage&q=%2230%2C300%20wounded%20and%20about%203%2C500%20missing%22&f=false The encyclopedia of modern war By Roger Parkinson] Taylor & Francis, {{আইএসবিএন|0-8128-1898-9}}. Page 133.</ref><br />30,300 wounded<br />'''Slovakia''':<br />37 killed,<br />11 missing,<br />114 wounded<ref name="Axis Slovakia: Hitler's Slavic Wedge, 1938-1945">"Axis Slovakia: Hitler's Slavic Wedge, 1938-1945", page 81</ref><br /> |
||
---- |
---- |
||
'''USSR''':{{#tag:ref|Soviet official losses are estimated at 737 to 1,475 KIA or MIA (Ukrainian Front – 972, Belorussian Front – 503, and 1,859 to 2,383 WIA (Ukrainian Front – 1,741, Belorussian Front – 642). The Soviets lost approximately 150 tanks in combat of which 43 as irrecoverable losses, while hundreds more suffered technical failures.<ref name="Krivosheev">Кривошеев Г. Ф., ''Россия и СССР в войнах XX века: потери вооруженных сил. Статистическое исследование'' (Krivosheev G. F., ''Russia and the USSR in the wars of the 20th century: losses of the Armed Forces. A Statistical Study'' Greenhill 1997 |
'''USSR''':{{#tag:ref|Soviet official losses are estimated at 737 to 1,475 KIA or MIA (Ukrainian Front – 972, Belorussian Front – 503, and 1,859 to 2,383 WIA (Ukrainian Front – 1,741, Belorussian Front – 642). The Soviets lost approximately 150 tanks in combat of which 43 as irrecoverable losses, while hundreds more suffered technical failures.<ref name="Krivosheev">Кривошеев Г. Ф., ''Россия и СССР в войнах XX века: потери вооруженных сил. Статистическое исследование'' (Krivosheev G. F., ''Russia and the USSR in the wars of the 20th century: losses of the Armed Forces. A Statistical Study'' Greenhill 1997 {{আইএসবিএন|1-85367-280-7}}) {{ru icon}}</ref>|group="Note"}}<br />1,475 killed or missing,<br />2,383 wounded |
||
| casualties2 = '''Poland''':{{#tag:ref|Various sources contradict each other so the figures quoted above should only be taken as a rough indication of losses. The most common range brackets for casualties are: Poland: 63,000 to 66,300 KIA, 134,000 WIA.<ref name="ReferenceB"/>. The often cited figure of 420,000 Polish prisoners of war represents only those captured by the Germans, as Soviets captured about 250,000 Polish POWs themselves, making the total number of Polish POWs about 660,000–690,000. In terms of equipment the Polish Navy lost 1 destroyer ([[ORP Wicher (1928)|ORP ''Wicher'']]), 1 minelayer ([[ORP Gryf|ORP ''Gryf'']]) and several support craft. Equipment loses included 132 Polish tanks and armoured cars 327 Polish planes (118 fighters))<ref name="ReferenceC"/>|group="Note"}}<br />66,000 dead,<br />133,700 wounded,<br />694,000 captured}} |
| casualties2 = '''Poland''':{{#tag:ref|Various sources contradict each other so the figures quoted above should only be taken as a rough indication of losses. The most common range brackets for casualties are: Poland: 63,000 to 66,300 KIA, 134,000 WIA.<ref name="ReferenceB"/>. The often cited figure of 420,000 Polish prisoners of war represents only those captured by the Germans, as Soviets captured about 250,000 Polish POWs themselves, making the total number of Polish POWs about 660,000–690,000. In terms of equipment the Polish Navy lost 1 destroyer ([[ORP Wicher (1928)|ORP ''Wicher'']]), 1 minelayer ([[ORP Gryf|ORP ''Gryf'']]) and several support craft. Equipment loses included 132 Polish tanks and armoured cars 327 Polish planes (118 fighters))<ref name="ReferenceC"/>|group="Note"}}<br />66,000 dead,<br />133,700 wounded,<br />694,000 captured}} |
||
{{Campaignbox Polish September Campaign}} |
{{Campaignbox Polish September Campaign}} |
||
২২:১৯, ৭ জুলাই ২০১৭ তারিখে সংশোধিত সংস্করণ
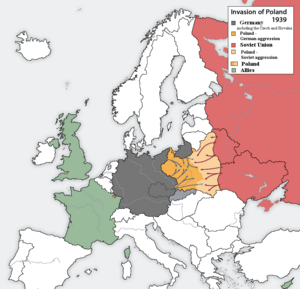
ভার্সাই চুক্তি অনুসারে জার্মানির ডানজিগ বন্দরের মালিকানা দিয়ে দেয়া হয়েছিল রাষ্ট্রপুঞ্জকে [league of nations]।১৯৩৯ এর ২১ শে মার্চ হিটলার ডানজিগের মালিকানা এবং ঐ পর্যন্ত যাবার জন্য পোল্যান্ডের ভেতর দিয়ে সড়ক ও রেলপথ দাবী করেন ।পোল্যান্ড দাবী অগ্রাহ্য করায় যুদ্ধের সম্ভাবনা তৈরি হল । সোভিয়েত ইউনিয়নকে নিষ্ক্রিয় রাখার জন্য জার্মানী অনাক্রমণ চুক্তি [non-aggression treaty] করে ।এই চুক্তিতে গোপণে ভাগবাঁটোয়ারার খসড়াও করা হয় । অন্যদিকে ব্রিটেন ও ফ্রান্স পোল্যান্ডের সাথে সহায়তা চুক্তি করে । ১লা সেপ্টেম্বর সীমান্তে একটি সাজানো আক্রমণের ছুতো ধরে হিটলার পোল্যান্ড দখলের অভিযান শুরু করল ।৩রা সেপ্টেম্বর মিত্রবাহিনী জার্মানীর বিরুদ্ধে যুদ্ধ ঘোষণা করল,এবং শুরু হল দ্বিতীয় বিশ্বযুদ্ধ । পোলিশ বাহিনী আয়তনে যথেষ্ট বিশাল হলেও তাদের অস্ত্রশস্ত্র ও সামরিক চিন্তাভাবনা ছিল সনাতন ।প্রথম দিনই জার্মান বিমান বাহিনী বোমা ফেলে তাদের শহর ,রেল ,সেতু ,শক্তিকেন্দ্র এবং তাদের বিমান বাহিনী অচল করে দিল ।অন্যদিকে সাইলেশিয়া ,প্রুশিয়া ,মোরাভিয়া ,স্লোভাকিয়া দিয়ে জার্মান বাহিনী ঢুকে পোলিশ বাহিনীকে ছিন্নবিচ্ছিণ্ন করে দিল ।ফরাসি ও ব্রিটিশ বাহিনী সাহায্য করবার সুযোগ পেল না ।এটি পশ্চিমের বিশ্বাসভঙ্গতা হিসেবে পরিচিত । জার্মানীর এই নতুন ধরনের যুদ্ধ পদ্ধতি blitzkrieg বা ঝটিকা যুদ্ধ নামে পরিচিত । ১৭ই সেপ্টেম্বর গোপন সমঝোতা অনুসারে সোভিয়েত বাহিনীও আক্রমণে যোগ দিল । পরদিনই পোলিশ কর্তাব্যক্তিরা দেশ ছাড়লেন ।ওয়ারস পতন হলো ২৭শে সেপ্টেম্বর ।শেষ সেনাদল কক্ দুর্গে যুদ্ধ করে ৬ই অক্টোবর পর্যন্ত । পোল্যান্ড অবশ্য আনুষ্ঠানিকভাবে আত্মসমর্পণ করেনি ।অনেক পোলিশ মিত্র বাহিনীতে যোগ দেয় এবং অনেকে যুদ্ধ শেষ হওয়া পর্যন্ত গেরিলা যুদ্ধ চালিয়ে যায় ।
তথ্যসূত্র
- ↑ ক খ গ Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The 1939 Campaign Polish Ministry of Foreign Affairs, 2005
- ↑ E.R Hooton, p85
- ↑ ক খ Кривошеев Г. Ф., Россия и СССР в войнах XX века: потери вооруженных сил. Статистическое исследование (Krivosheev G. F., Russia and the USSR in the wars of the 20th century: losses of the Armed Forces. A Statistical Study Greenhill 1997 আইএসবিএন ১-৮৫৩৬৭-২৮০-৭) (রুশ)
- ↑ ক খ গ Переслегин. Вторая мировая: война между реальностями.- М.:Яуза, Эксмо, 2006, с.22; Р. Э. Дюпюи, Т. Н. Дюпюи. Всемирная история войн.—С-П,М: АСТ, кн.4, с.93
- ↑ Internetowa encyklopedia PWN, article on 'Kampania Wrześniowa 1939'
- ↑ Website of the Polish Ministry of Foreign Affairs – the Poles on the Front Lines
- ↑ ক খ Wojna Obronna Polski 1939, page 851
- ↑ ক খ "Polish War, German Losses"। The Canberra Times। ১৩ অক্টো ১৯৩৯। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০০৯-০১-১৭।
- ↑ "Nazi Loss in Poland Placed at 290,000"। The New York Times। ১৯৪১। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০০৯-০১-১৬।
- ↑ ক খ গ ঘ KAMIL CYWINSKI, Waffen und Geheimwaffen des deutschen Heeres 1933-1945
- ↑ The encyclopedia of modern war By Roger Parkinson Taylor & Francis, আইএসবিএন ০-৮১২৮-১৮৯৮-৯. Page 133.
- ↑ "Axis Slovakia: Hitler's Slavic Wedge, 1938-1945", page 81
উদ্ধৃতি ত্রুটি: "Note" নামক গ্রুপের জন্য <ref> ট্যাগ রয়েছে, কিন্তু এর জন্য কোন সঙ্গতিপূর্ণ <references group="Note"/> ট্যাগ পাওয়া যায়নি